My BEST Dentists Journal
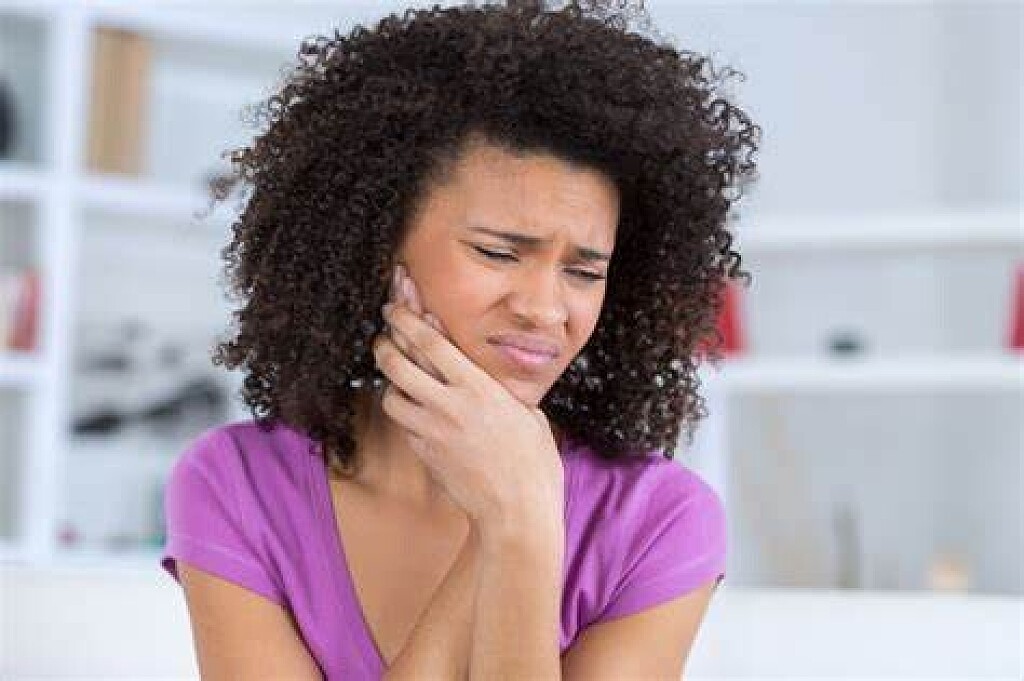

Why Does My Jaw Hurt on Only One Side?
While sleeping, you’re jolted awake by a sudden pain on only one side of your jaw. Although the situation can be alarming and confusing, don’t worry – it typically isn’t a cause of immediate concern. However, that doesn’t stop the questions from running through your head. What does it mean? When should you see a dentist? How can you alleviate the discomfort? Luckily, we’ve got all the answers you’re searching for and more – just keep reading!
What Causes Jaw Pain?
There are several reasons why you may experience jaw pain on one side, including:
TMJ Disorders
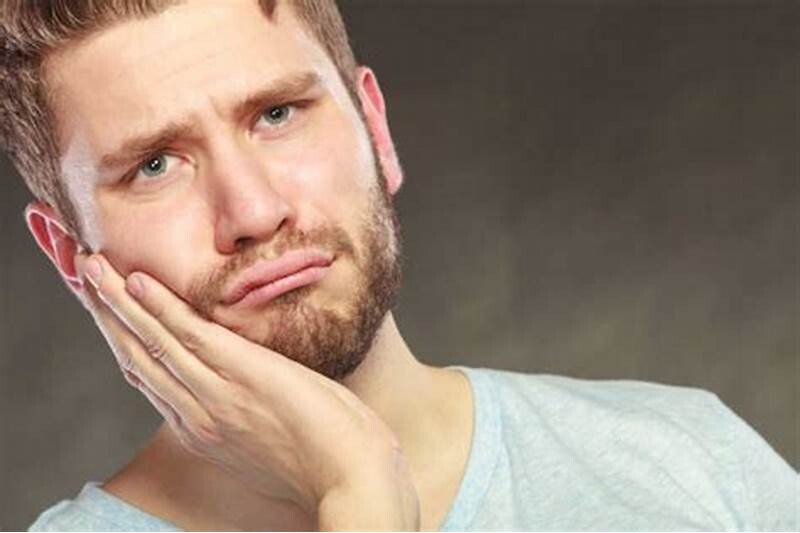

A temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder affects the joint that connects your skull and jaw. A disc separates the bones in this joint and helps it move properly. If it becomes misaligned or the joint is damaged, you might experience pain and other symptoms like tenderness, earaches, clicking or popping when opening your mouth, difficulty opening and closing your mouth.
Oral Health Problems
In some cases, jaw pain on one side can indicate underlying oral health problems. Some common issues that cause jaw pain are cavities, an abscessed tooth, gum disease, tooth decay, growth of wisdom teeth, missing or crooked teeth, and clenching or grinding your teeth.
Sinusitis
Inflammation in your nasal cavities can cause sinusitis. Since the nasal cavities are located behind the cheeks, inflammation can cause pain in one or both sides of your jaw. Usually, this pain is accompanied by other symptoms like nasal congestion, yellow or green mucus, facial swelling, fatigue, and difficulty smelling or tasting.
When to See a Dentist
As mentioned earlier, jaw pain on one side isn’t usually considered a dire situation. But if the discomfort is accompanied by other symptoms, it could indicate a more severe condition – one that will require immediate treatment.
If you experience any of the following, contact your emergency dentist right away:
A persistent or recurring pain that doesn’t go away within a few days
Difficulty eating, drinking, swallowing, or breathing
Swelling or a fever that doesn’t go away
Significant pain that vanishes after a burst of salty liquid that tastes and smells unpleasant
How to Alleviate Jaw Pain
Do you have mild pain in your jaw? You may not need medical treatment! Here are a few ways you can get relief:
Apply a hot or cold compress. Heat can help your muscles relax, giving you relief from aches and stiffness. Alternatively, a cold compress can numb the pain and reduce swelling.
Take over-the-counter pain relief. Medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) can temporarily relieve your pain.
Rest your jaw as much as possible. Stick to a diet of soft foods that don’t require a lot of chewing. It’ll help you avoid overworking your jaw muscles!
Massage your jaw. It can help release pain and tension in your jaw. Try some techniques on your own or visit a specialist for help (i.e., healthcare provider, physical therapist, massage therapist).
If you’re experiencing jaw pain on one side, use the tips outlined above for some relief. Although it should typically resolve on its own within a few days, you can always seek treatment from your dentist for peace of mind!
(12/27/2025)by Zumbro Family Dental
More Information: N
Views: 1,572
Got Food Stuck in Your Teeth?
Few things feel more satisfying than finishing a good meal. But this positive feeling can sour if you are left with bits of food stuck between your teeth. It may feel hard to resist trying to free the trapped food with your tongue, and this can distract you from other activities on your agenda.
But trapped food between your teeth is more than just annoying. Lingering food particles in your mouth can also pose a threat to your dental health. So you should not ignore this oral phenomenon if you want to protect your smile. Read on to learn more about what food stuck in your smile means for your oral health.
Does Trapped Food Hurt My Oral Health?
Most people associate food stuck in the teeth with a pesky foreign presence within the mouth. But if food stays trapped between the teeth, your mouth might start to feel sore as well. Trapped food can apply pressure on the tooth which can lead to this chronic ache.

You should not try to tolerate or ignore this sensation. The pressure may indicate that the teeth are starting to shift out of their straight alignment. To preserve the look and feel of your smile, you should address this issue promptly.
Lingering food in your smile will also start to decay after a while. This encourages natural oral bacteria to produce plaque. And as food particles and plaque form, they will start to eat away at your dental structure.
Then you will have a high risk of forming cavities and many other dental dangers. Prevent dental emergencies by getting rid of trapped food between teeth as soon as you can.
How Do I Safely Remove Food from Between Teeth?

You can take action to remove food from your teeth on your own, though you should stick to recommended methods of doing so. You may feel tempted to dig the food out with fingernails, but this is not a polite act to do in public. Also, it is unsanitary to put germy fingers in your mouth and then transfer oral bacteria to your hands.
Instead, dentists suggest using dental floss or a toothbrush to free the food stuck between the teeth. Your oral hygiene regimen is designed to scrub away residues from your smile in a safe and effective way. Floss in particular targets the space between the teeth so that you can eradicate these harmful particles without hurting the rest of your smile.
Can I Prevent Food Trapped in My Smile?
A small seed or bit of pork might stick in anyone’s smile every now and then. But if you often have trouble with food in the spaces between your teeth, you might have what dentists call a food trap.
These refer to changes in the spacing between teeth, whether due to issues with the gums or alignment concerns in the teeth, where food will easily get stuck. You should talk to your dentist if you notice this problem so that they can offer treatment to stop this from happening going forward.
(12/26/2025)by Reedy Creek Family & Cosmetic Dentistry
More Information: N
Views: 1,438
Using a Floss Threader: Flossing Made Easier
Many are aware that flossing is a vital step in your oral care, but fewer know what tools are available to make it less of a chore. Floss threaders might be what you've been looking for if you have braces, a permanent retainer, a bridge or another orthodontic device. We're here to help navigate why flossing is important and how to do it correctly with a threader.
Why Floss?
Cleaning between your teeth with floss or a flossing device is an essential part of your dental care routine, especially if you have a dental appliance. Why is flossing so important? The best way to care for your oral health is to avoid problems before they start.
Cleaning between your teeth removes food debris and plaque, preventing cavities and gum disease. If plaque isn’t cleaned, it hardens into tartar that requires a dental professional's help to remove. Food matter that is not adequately removed will contribute to bacterial growth and tooth decay.
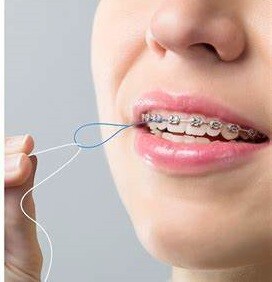
Remember that the most important part of flossing is not about the type you use but that you do it effectively and regularly. By educating yourself on proper flossing technique and making it part of your daily routine, you’re taking a great step forward for your oral health.
Tips for cleaning between your teeth effectively:
Choose a time of day that’s convenient for your schedule to floss so that you can devote proper time and attention to the task.
Don’t reuse floss as it could be damaged or contain harmful bacteria.
Schedule regular visits to your dentist.
What Are Floss Threaders?
The Ministry of Health recommends flossing once a day and brushing twice a day. This part of your routine can be especially challenging if you have an orthodontic device like braces, a permanent retainer or a bridge.
Luckily, floss threaders are here to help.
These helpful tools make it easier to floss effectively for those who find it difficult due to their dental appliance or other challenges. Not only can it be an ordeal to clean difficult-to-reach areas, but braces and other devices can fray the floss and force you to start over.
Floss threaders are loops of thin material that make it easier to clean difficult-to-reach areas of your teeth and gums with floss. They’re disposable, work with any regular floss, and are easy to find online or at any store with a dental section.
Helpful tip: If you’re having trouble finding a flossing device that works for you, it’s a good idea to consult your dental professional. It’s also a good idea to schedule an appointment with the pros if you’re experiencing pain or bleeding when flossing regularly.
How to Use a Floss Threader
Flossing with a threader is much like flossing normally but may take extra time and effort as you master the technique. You’ll be glad to have made the extra effort to avoid health problems down the line like cavities or gum disease that will require the help of a dental professional to treat.
How to properly use a floss threader:
Break off between 30 to 45 cm of your favourite floss.
Run approximately 12 cm of one end of the floss through the loop of the threader.
Run the floss threader through your dental appliance and into a gap between your teeth.
Remove the loop of the threader and floss normally. Press the floss into your gum line, form it into a C-shape, and run it gently up and down the sides of both teeth.
Repeat for each tooth, including the outside of your back teeth. Discard the threader after use.
If this process sounds challenging, don’t worry! Keep in mind that it will get easier with practice; the first time is always the most difficult. Cleaning between your teeth is a vital step in your dental routine, and floss threaders may be the tool you’re missing to make flossing easier. You’re now set up for success after informing yourself on the best way to use floss threaders.
(01/09/2025)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-sg/oral-health/brushing-and-flossing/using-a-floss-threader-make-flossing-easier
Views: 1,749
How to Pull a Loose Tooth That Won’t Come Out
A loose tooth can be very annoying and discomforting. Your oral hygiene, gum disease, teeth grinding, hard food, mouth injury, anything can result in a loose tooth. You can let your tooth come out on its own. But the issues that come with that, like problems in eating food, constant sensitivity, etc can be hard to bear. And you just can’t keep waiting for your tooth to fall on its own for a long time. So, how to get a tooth out in a fast and painless way?
How to pull an adult tooth out without pain?
There are a few ways through which you can pull out a loose tooth without hurting yourself. However, if you are experiencing any kind of inflammation or pain, it is advisable that you visit a dentist.
1. Wiggle your tooth
Continuously wiggling your tooth back and forth using your tongue or clean hands will loosen it up. And it will come out eventually, on its own. However, don’t wiggle it too hard or it will hurt. And if you feel any kind of discomfort while wiggling it, see your dentist immediately.
2. Chew on hard food
Chewing on hard foods like apples, carrots, pears, etc will considerably loosen the already loose tooth. Usually, this process is quick and painless. Start with something a little softer and gradually move to something crunchier. You can also bite into an ice pop and pull out the tooth gently while your gum is still numb from the ice.
3. Brushing and flossing

Regular brushing and flossing will also help you pull an adult tooth out without pain. Don’t brush or floss too hard or it can get painful. When you are flossing, gently guide it between your loose tooth and the one next to it. Curve the floss around the bottom of your loose tooth. Also, run your floss up and down each side of your loose tooth. Doing it every day will loosen up the tooth even more and help it come out painlessly.
4. Wet wash cloth or gauze
Use a cold and wet washcloth or gauze to hold and remove the loose tooth gently. If your tooth is not loose enough to come out painlessly, keep wiggling it while holding it with a wet cloth or gauze. When you think the tooth is loose enough, give a gentle tug. The tooth will come out easily and the gauze will help in stopping the bleeding if any.
5. Sucking on ice chips
Sucking on ice chips will help the gums around the loose tooth to get numb. It will prevent you from feeling the pain when you gently pull it out. After you have pulled out your tooth painlessly, keep sucking on ice chips for ten minutes thrice or four times a day to numb the pain. Don’t keep sucking on ice continuously or it will damage your gum tissue.
6. Teething gel
You can use aesthetical gel with benzocaine to numb the tooth socket. This could be very useful if wiggling the tooth is causing pain. Read the manufacturer’s instructions carefully before using the gel. Apply it to your gums, wait for the gel to numb your gums, and then pull out the tooth gently.
7. Use tweezers
You can use tweezers to wiggle the tooth free. If you are not able to pull out the loose tooth without hurting, don’t apply force. You can repeat the process after wait for a few days. When you feel the tooth is loose enough to come out easily, give it a gentle tug.
These are a few ways to get a tooth out in fast and painless ways. But the process doesn’t stop here. Aftercare of your gum is very important.
Aftercare tips after pulling out a tooth
Pulling out a tooth can be quite painful and finding a little blood on the spot is common. Here are a few care tips after pulling out the loose tooth.
1. Use sterile gauze
Apply a little pressure on the tooth socket using sterile gauze to stop the bleeding. The bleeding should stop in a few minutes. You can also press it gently using the upper tooth.
2. Wet teabag
Wet teabag can also come in handy for soothing the gum after pulling the tooth out. Steep the teabag in hot water for a few minutes, squeeze out the excess water, let the teabag cool down for a few minutes and apply it to the tooth socket to dull the pain. You can use chamomile, black, green, or peppermint teabags to soothe the pain.
3. Over-the-counter pain relief medicine
It is not easy to pull out the loose tooth without hurting. If you are still experiencing pain, you can take pain killers like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, etc. Make sure you read the manufacturer’s instructions before taking the medicine. Or, even better, ask your doctor if you are not sure about taking them.
4. Wait for 24 hours before rinsing
After pulling the tooth, there will be a blood clot in the tooth socket. This clot will help the area to heal properly hence it is vital to let it remain in place for 24 hours at least. So, wait for that time before rinsing your mouth. Use a straw to drink water and avoid anything that can result in suction or vigorous rinsing.
Additional tips
Don’t brush or floss the socket of the tooth you have just pulled out, or the area around it.
Rinse gently but don’t swish vigorously.
Don’t consume anything too cold or too hot. For two days, eat soft food and consume everything at room temperature.
Use toothpaste with fluoride and mouthwash two times a day.
Avoid smoking and consuming tobacco.
If you are still feeling pain or sensitivity even after two-three days of pulling the tooth out, visit your dentist.
Try not to pull out your loose tooth until it is absolutely necessary. In case of any discomfort, pain, swelling in gums, and inflammation, visit your dentist immediately.
(01/08/2025)by Healthgree
More Information: https://healthgree.com/dental-health/how-pull-loose-tooth-wont-come-out/
Views: 1,579
Do Dentures Make Your Mouth Dry?
Dentures do not technically cause you to have “dry-mouth,” but when you have dry mouth and wear dentures, the affects can be much more noticeable and irritating. Dry mouth can be frustrating and can cause issues when wearing or trying to use your dentures for practical uses. If dry mouth persists or is extremely bad, it can lead to other health problems. The good news is that there are treatments and processes that can reduce or eliminate this problem.
What is dry mouth?
Dry mouth or xerostomia is a condition in which the salvatory glands in your mouth are not producing enough saliva to keep your mouth wet. Dry mouth can be caused by a variety of different conditions and circumstances. Dry mouth can range from just being irritating, to something that is strongly impacting your well-being.
Saliva is important because it enhances your ability to chew and swallow food (it also helps enhance taste of food), it helps aid in digestion as there are enzymes in saliva that help break down food and neutralize bacteria, and it also helps prevent issues such as tooth decay by limiting bacteria growth and washing away food particles from gums and teeth.
Dry mouth can cause a feeling of dryness and/or stickiness in your mouth, it can cause bad breath and sore throats, it can make chewing, talking, and swallowing difficult. It can also cause cracking at the corners of the mouth, bleeding gums, and dry or bumpy tongue.
Why is dry mouth problematic for denture wearers?
Dry mouth is annoying, but even more so for denture wearers. When wearing dentures and struggling with dry mouth, you may notice that your dentures are not suctioning to your gums properly; that is because saliva acts like a glue to keep your dentures retained against your gums.
Dry mouth also makes you more prone to bacterial and fungal mouth infections such as angular cheilitis, oral stomatitis, and thrush. Thrush, for example, can cause white lesions in your cheeks and tongue. It can cause soars and make it difficult to eat. When struggling with an oral infection, it can be very uncomfortable to wear and use your dentures.
Not only are health issues associated with dry mouth and dentures, but dry mouth can cause your dentures to dry out. When dentures dry out, they can become brittle and warped, and are more likely to break, which will result in needing a new pair. If you suffer from dry mouth, it is extra important to take your dentures out at night and put them in a hydrating cleaning solution.
What causes dry mouth?
Many different circumstances can bring about dry mouth including:

Your age
As we age, the saliva glands in our mouths start to slow down and produce less saliva.
Medications, illnesses, and cancer treatments
Certain medications, illnesses, and cancer treatments have side effects such as dry mouth.
Nerve damage
Injuries to nerves in the head or neck can cause dry mouth as some nerves carry messages from the brain to the salivary glands; when damaged, they may not carry these messages to the brain.
Smoking
Smoke, as well as nicotine in tobacco reduces saliva flow.
Mouth breathing
As a mouth breather you are more likely to have dry mouth as the air constantly flowing through your mouth can cause saliva to evaporate or produce at a much slower rate.
Sugary diet and diabetes
Increased blood sugar can cause dry mouth.
What are the solutions for dry mouth when wearing dentures?
The cause of your dry mouth will determine what type of treatment options you need to seek.
Some of the general steps you can take to combat dry mouth include, but are not limited to:
Staying hydrated
Hydration is a major factor that can contribute to dry mouth. If you are not drinking enough water or are consuming too many sugary drinks, you may find your mouth drying out.
Avoid dry foods and drinks
Dry foods such as crackers, breads, and pastries, and drinks that contain caffeine or alcohol can contribute to the drying of your mouth.
Avoid tobacco and other smoke products
As mentioned, nicotine and smoke contribute to a dry mouth.
Avoid mouth breathing
The constant flow of air through your mouth can cause saliva to evaporate or produce slower.
Alternative or complimentary medications
If you are taking medications that cause dry mouth, talk to your doctor about alternatives and medications that can aid in saliva production (never stop taking your prescribed medication without talking to your doctor).
Dental implants
Consider dental implants. These can help reduce dry mouth as the implant posts increase the integrity of the jawbone, this can help encourage saliva production.
(01/08/2025)by Olds Denture And Implant Centre
More Information: N
Views: 1,556
Four Things To Always Remember: About Your Tongue!
Did you know that along with the other parts of your smile, as you’re striving to keep your smile health in exceptional condition, you should keep your tongue in mind along the way? If you’re shrugging your shoulders because this is truly something you’ve been overlooking, then remember: It’s never too late to add new knowledge to your already significant collection of important smile-related facts that help you keep your grin safe and sound! Make sure you’re confident about this area of oral health care by considering our Overland Park, KS team’s suggestions for things you should always remember.
#1: It Needs To Be Cleaned, Too!
We realize you may have the idea in your mind, which may have been there for many years already, that dental hygiene that is complete is hygiene that includes brushing your teeth and flossing between them. With that said, we must now inform you that you’re almost there. However, what you’re missing is the fact that you need to also pay attention to the tissue along the top surface of your tongue, if you wish to keep your oral health in lovely condition. Add this to your mental list of smile requirements now!
#2: You May Brush It Or (Gasp!) Scrape It

Brush your tongue, as you brush your teeth. Or, use a tongue scraper. Either will work just as well!
#3: A Dirty Tongue Contributes To Bad Breath, Etc.
Remember that protecting your smile from an accumulation of bacteria, which can lead to oral health problems, means removing it from your entire mouth, not just teeth and gums. When you ignore your tongue and you don’t keep it clean, the bad bacteria that build up will contribute to a host of unpleasant issues, such as bad breath. Follow our suggestions for protecting your smile with complete dental hygiene (as in, brush your tongue, too) and enjoy the benefit of fresh-smelling breath!
#4: If You Notice Changes, It’s Time To See Your Dentist!
It’s not always easy to know what’s going on inside your mouth, which is why we always encourage you to contact our team to schedule a dental checkup for anything that changes. While you may assume this is primarily for your gums and teeth, remember that you are invited to come in with questions about all of your mouth, including your tongue and other tissues! Don’t ignore changes. Come in. The sooner you do, the easier it will be for us to help you!
(01/07/2025)by Family First Dental
More Information: N
Views: 1,524
What Happens When Lip Fillers Wear Off?
If the filler isn't permanent, such as Restylane Silk or Juvederm, the lips will return to their original shape, according to Dr. Howard Sobel, founder of DDF Skincare. Permanent fillers, such as Silicon 1000, will remain unchanged. The skin of the mouth and lips will return to its normal appearance without sagging or stretching.
This change will occur gradually; you won't wake up one morning to find that you've suddenly lost volume. As the filler fades, your lips may look somewhat aged as the normal aging process continues. Body+Beauty Lab always recommends starting lip augmentation with a small amount of filler and then slowly increasing the amount as desired. If you are somehow dissatisfied with the results of your lip injection or want to return to your previous appearance, we can easily reverse your result after lip injections.

Products containing hyaluronic acid can be partially or completely dissolved through an enzyme called hyaluronidase. In turn, the muscles will temporarily relax and cause the lip to move upwards to create the illusion of defined and thick lips. Over time, fillers will slowly decrease in fullness before taking their original shape and will not “deform” at all. On average, fillers are supposed to last six to nine months, but because the lips are more mobile on a daily basis, they can sometimes be a little less.
The amount of lip filler can be controlled, so the results are more accurate compared to implants. During a lip change, a trained Botox provider will skillfully inject the toxin into the orbicularis muscle (the muscle surrounding the mouth) just above the upper lip area. Since lip fillers are created using natural enzymes, the body processes them over time. Unfortunately, some people hesitate to put on lip fillers because they have questions about treatment.

Lip threading or lip flossing is a technique that uses dissolvable threads to soften the folds and lines shown around the mouth. Regardless of whether the type of dermal filler chosen increases collagen production, most of the time, no dermal filler will have any type of negative and lasting effect on your face.
But what can happen when you suddenly decide to stop Botox treatments? Botox lip injections work by relaxing the muscles in the upper lip area so that they bend upwards and achieve a smooth appearance.
(01/06/2025)by lip-fillers-hub.com
More Information: N
Views: 1,658
Dental Technology: The Professionals Who Restore Smiles
Dental technology is a branch of the dental sciences that includes dental technicians, lab scientists, metallurgists and other compound specialists who work to recreate dental anatomy. Whether the natural oral environment is disrupted by disease, accidents or other alterations, skilled professionals can help restore the function, health and look of their patients' mouths.
Who Are Dental Technicians?
Dental technicians use their artistic and scientific talents to construct prostheses after obtaining a prescription and dental impressions from a licensed dental professional. By using materials available in the industry, dental technicians can improve the quality of life for patients by restoring or retaining their natural smiles through the replacement of missing or damaged teeth and gums.
The dental technician collaborates with the dental office to design safe reconstructive devices, such as crowns, bridges, full dentures, partial dentures, ceramics or veneers, orthodontic appliances and implants. The cost of these devices varies greatly depending on the time, work and materials that go into each one. For dentures, in addition to the initial purchase price, any repairs must also be factored into the overall price tag.
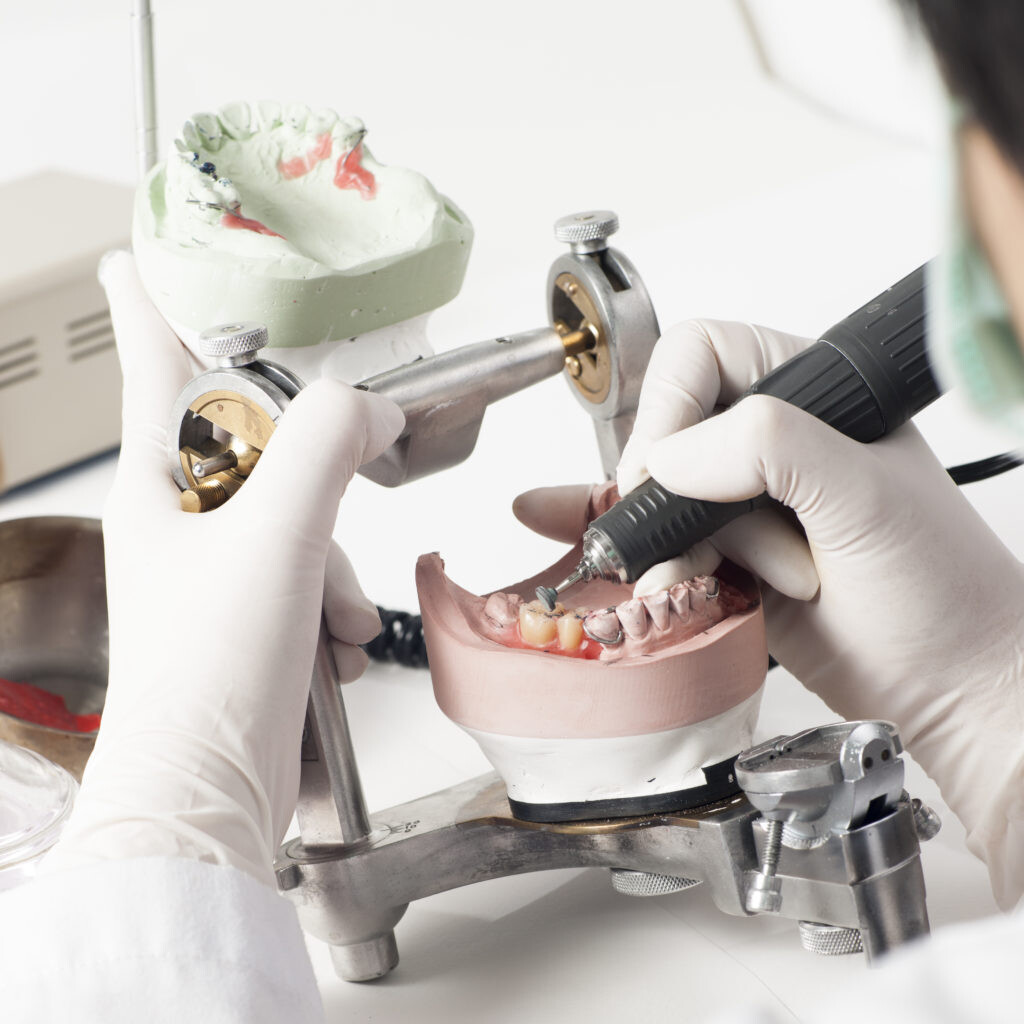
What Type of Education Do Dental Technicians Need?
To award an associate degree in dental technology, most educational programmes require two years of study. During this two-year programme, students become experts in the creation of dental restorations, appliances for tooth movement, or any one of the various modalities for tooth replacement that can be fitted onto dental implants or natural tooth structures.
A dental technician is formally trained at a recognised institution to an NQF level 6 qualification in dental technology, and is registered with the South African Dental Technicians Council.
Dental Lab Technology in Action
Dental technology is a rapidly changing field. Through new CAD/CAM (computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing) techniques and improved treatment options, patients are keeping their teeth longer in life. According to a survey 48 percent of adults aged 20 to 64 had retained all their teeth in 2011-2012. Nevertheless, that means a large percentage of the population still needs the expertise of dental technicians.
(01/06/2025)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/dental-visits/dental-technology-the-professionals-who-restore-smiles
Views: 1,459
Things That Can Make Chapped Lips Worse, According To Dermatologists
It’s officially chapped lips season. And let us tell you, we feel your pain.
One of the worst side effects of dealing with cold weather is dealing with dry, cracked, painful lips. Sometimes, it feels like no amount of lip balm can help.
Some people have even questioned whether lip balm is the problem. According to the pros, however, that’s a myth, as long as your lip balm contains the right mix of ingredients. But more on that later.
There are, however, a few things that actually can make your chapped lips worse. If you’re one of the many people who struggle to keep your pout sufficiently moisturized, take note:

1. Licking your lips all the time
You’ve probably heard this one before, but just to enforce it one more time: Licking your lips when they’re already chapped isn’t doing you any favors.
Although it may seem like a good idea at the time, “as the saliva dries and evaporates, it draws moisture away from the skin,” Dr. Y Claire Chang, board-certified cosmetic dermatologist at Union Square Laser Dermatology, told HuffPost.
Excessively licking your already-dried out lips, as Dr. Benjamin Barankin, a Toronto-based dermatologist and medical director of Toronto Dermatology Centre, put it, leads to “short-term gain, long-term pain.”
Dr. Rachel Nazarian, of Schweiger Dermatology Group in New York City, elaborated: “Our saliva contains enzymes that make it effective for digesting our food when we eat. By licking your lips you apply the same digestive enzymes to your skin, and it can break down lips and make them dry and chapped.”
Licking your lips repeatedly can also get you caught in a cycle of wetting and drying the lips, and can even lead to something called “lip licker’s dermatitis,” which Chang described as “an irritant contact dermatitis around the lips characterized by redness and dryness around the lips.”
“The best way to treat dry lips is to avoid licking and, instead, apply bland emollients frequently to provide external hydration,” Chang added.
2. Cleansing with hot water
We’ve been told that super hot water isn’t great for keeping your skin moisturized, so it only makes sense that it won’t help dry lips. In fact, it can actually make dry lips worse, Chang said.
“Although hot water feels nice in the short-term, it can actually draw out moisture from the lips as it evaporates,” she added.
Barankin also noted that hot water strips away the natural oils that keep lips moisturized. To keep your lips from drying out, Nazarian recommended using lukewarm water and gentle cleansers when washing your face “to prevent your skin from drying out, especially in arid and cold weather months.” And that applies to your time in the shower, too, when hot water will come in contact with your lips.
3. Exposure to the sun
“Sun exposure can worsen chapped lips, so it is important to wear lip balm with SPF to keep your lips protected, especially when out in the sun,” Chang advised.
4. Flavored lip balms
All three dermatologists we spoke to agreed that fragrances, which are commonly found in lip balms, can irritate the skin and increase the potential for chapping.
It’s best to avoid using any products with fragrance, Nazarian said. She suggested applying a lip balm with lanolin or beeswax with no added colors or perfumes to prevent evaporation of moisture from the lips. Vaseline, which contains white petrolatum, is also effective, she said.
5. Irritating ingredients
Not all lip balms are created equal.
“I recommend avoiding excessive use of lip balms with salicylic acid, which is an exfoliant that removes dead skin cells,” Chang said. “Too frequent use of salicylic acid can cause irritation and further dry out the lips.”
Other ingredients to avoid are menthol or peppermint ― commonly added to lip balms for that cooling, soothing sensation ― Nazarian said. She also recommended steering clear of cinnamic aldehyde, the chemical compound that gives cinnamon its flavor, which can cause irritation in sensitive skin.
So what’s the best way to keep lips hydrated?
We’ll start by saying this: all three dermatologists said there’s really no such thing as applying too much lip balm, so long as you’re using something with the right ingredients.
Nazarian suggested using a product that contains hydrating ingredients (like ceramides and hyaluronic acid) along with ingredients that seal in moisture (like lanolin, petrolatum or beeswax) for “the perfect combo for soft, hydrated lips.”
Barankin recommended using a bland chapstick twice a day and urged not to lick or pick at your lips. If you need to put some moisture back into your lips, he also said you can put a damp cloth with warm water over the area followed by a proper lip balm to lock it all in.
In Chang’s opinion, if you’re using a lip balm to hydrate and lock in moisture, free from irritating ingredients, it’s “the more, the better.” It’s also wise to drink more water and use a humidifier at home to keep moisture in the air during the cold, dry winter months, she added.
You should also note:
If you’ve been treating your lips with care but continue to experience irritation and dryness, it might be a sign of an underlying issue, Chang said.
“Dry, chapped lips can sometimes be a sign of vitamin deficiencies, inflammatory bowel disease, fungal infections, contact dermatitis, excessive sun-damage, ill-fitting dentures or medication side effects,” she added, noting that it’s “important to address any underlying issues and medical conditions that may be causing dry lips.”
(01/04/2025)
by HuffPost Style & Beauty
More Information: N
Views: 1,476
Identifying The Cause of Persistent Toothache
Toothache can disrupt your comfort in several ways, as the pain can be unbearable and affect your ability to eat, drink, speak, and even sleep. It can cause significant discomfort, leading to poor performance at school or work, mood swings, and decreased quality of life. The increased sensitivity to hot and cold food and drinks that often accompanies toothache New York can also be an added discomfort. The annoying pain can be due to several factors, each requiring a unique treatment approach.
Tooth decay
As tooth decay progresses, it can reach the softer inner layers of the tooth, called dentin and pulp, resulting in sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks and eventually leading to a toothache. If left untreated, tooth decay can result in an abscess, a painful infection at the root of the tooth that can cause severe pain and swelling. Adhering to your routine dental check-ups, practicing good oral hygiene, and eating a healthy diet can help prevent tooth decay and the resulting toothache.
Abscessed tooth
An abscessed tooth occurs when the pulp inside your tooth becomes infected, typically due to decay or damage. The infection can spread to the tooth’s root and surrounding tissues, causing pain and swelling. In some cases, a pocket of pus may form in the affected area, leading to additional discomfort and even fever. Abscessed teeth may also cause sensitivity to hot or cold foods, a bad taste in your mouth, and difficulty chewing or speaking. If you have an abscessed tooth, inform your provider to prevent further complications and potential tooth loss.
Tooth fracture
A tooth fracture can expose the sensitive nerves and blood vessels inside your tooth, leading to pain and discomfort. The severity of your discomfort can vary, depending on the extent and location of the fracture. A small crack or chip may only cause mild discomfort, while a larger fracture may result in severe pain and sensitivity to hot and cold foods and drinks. In some cases, a tooth fracture can also lead to infection, further exacerbating the pain and requiring immediate dental treatment.

Repetitive motions
Repetitive motions like chewing or clenching your teeth can cause pressure and stress on your teeth and surrounding tissues. When you continuously subject your teeth to these motions, they may become sensitive or even develop cracks or fractures, which can expose the underlying nerves and cause pain. Clenching or grinding your teeth can cause wear and tear on the enamel, leading to tooth decay or gum disease, which can also cause toothache.
A damaged filling
A damaged filling can cause toothache when the filling is no longer able to protect your tooth from external stimuli. When a filling is damaged, it can create an opening in the tooth, allowing bacteria to penetrate and cause an infection, leading to inflammation, swelling, and pain. Additionally, if you don’t replace the filling in time, it may cause your tooth to weaken or crack. A damaged filling may also cause sensitivity to hot and cold food and drinks.
If you have a toothache, call the Compassionate Endodontists New York/NYC office or book an appointment online for diagnosis and treatment.
(01/04/2025)by Health Wiser
More Information: https://health-wiser.com/identifying-the-cause-of-persistent-toothache/
Views: 1,470
Why Are My Lips Dark Around The Edges?
Lips are one of the sexiest parts of the human body. It is one of the first things we notice when looking at a face.
Do you suffer from dark areas around the edges of the vermillion of your lips? Are you looking for a way to lighten these areas for aesthetic reasons? Read on, and I will tell you what is causing those dark areas and five easy ways to lighten those areas.
Both men and women can get these dark spots. There is a myriad of reasons why your lips may be dark. Let’s explore the most common ones.
Why Are My Lips Dark Around The Edges And How To Lighten Them?

Sun Exposure
Yes, going outside and getting some sun is great for our health and happiness, but we need to go out with the right protection for our skin, including our lips! These spots may be a result of a buildup of melanin (skin pigment) in these areas.
The condition is called hyperpigmentation (if you have dark spots on other parts of your face; this is the same reason why). People with higher melanin in their skin are more likely to have these spots. It’s ok to have fun in the sun, just bring the sunblock!
Birth Control
Even though birth control is amazing for plenty of other reasons, it could be the cause behind those dark areas around your lips. Birth control is linked to melasma, when melanocytes (aka, melanin cells) overproduce melanin, resulting in those pesky dark spots.
This is thanks to the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone; “the pill” is changing these hormone levels, resulting in those unfortunate dark spots. Keep in mind other medications may cause this too—so be sure to ask your doctor about side effects!
Post-Inflammatory Hyper-Pigmentation
This is a temporary condition that causes dark spots after an injury (burn) or inflammation (such as infection, dermatitis, etc.). It may become darker when exposed to UV light. Be aware that waxing and shaving can also cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation!
Hormone Disorder
Certain hormones (besides sex hormones) can cause hyperpigmentation. If you suffer from an endocrine disease, it could be contributing to this condition. Ask your doctor to test your hormones and if your condition may exacerbate hyperpigmentation.
Vitamin Deficiency
Did you know that what you eat can affect the color in your skin? Numerous studies have liked B12 deficiency with skin pigmentation issues. You may need to rethink your diet or start supplementing. Consult your doctor or registered dietician if you think you may have a vitamin deficiency.
Too Much Iron
Speaking of vitamins, too much of iron is NOT a good thing. Having too much iron is called hemochromatosis. This can cause iron to build up in the sweat glands of the body, causing a heavy bronze stain. While this condition is quite often underdiagnosed, it is also very rare.
Genetic Pre-Disposition
You could be genetically predispositioned to hyperpigmentation. That means if mom or dad had skin pigmentation issues, they most likely passed it on to you. But hey, there are worse things to pass on in genes, am I right?
Prevention
Prevention is key when it comes to preventing or worsening dark areas. Some things you can do include:
Stop taking birth control
Use more sun protection or stay out of the sun during peak hours.
Consult a physician to get your blood tested for hormones and vitamin deficiencies.
Thanks for stopping by! I hope you enjoyed reading this article about how to get rid of dark areas around your lips.
(01/03/2025)
by Nail Art Gear
More Information: N
Views: 1,483
Signs You’re Probably Not Drinking Enough Water
Nothing is more refreshing than a tall, ice-cold glass of water. It’s rare for anyone to dispute that a simple glass of water can provide more satisfaction than a coffee, soda, or even a can of coke. However, it’s common for people to ignore the former and go for the later, unwittingly causing damage to their bodies.According to a survey, about 75 percent of Americans are dehydrated, which is commonly ignored as people continue to deprive themselves of water and expose their system to serious health complications.
The body provides indicators to warn you when your body fluid level is at a level that can cause problems for you. When you detect any of these signs, drink a glass of water immediately.
Besides being thirsty, what are the signs that you’re not drinking enough water? Do you know that you’re getting enough water into your system?
Well, we will learn about the 9 signs of what could possibly happen if you aren’t drinking enough water. If that happens, it’s important to do everything to get your hydration level back on track.

Impaired Memory and Concentration
One of the reasons you find yourself unable to concentrate can be because you’re not drinking enough water; you are mildly dehydrated.
While it’s not exactly clear what causes these symptoms, researchers at the University of Connecticut Human Performance Laboratory attribute it to changes in the blood electrolyte balance due to dehydration. As a result of this, the brain’s part responsible for cognitive function and reasoning becomes impaired. Irregular blood electrolyte levels can also affect brain serotonin levels, leading to moodiness and anxiety.
The average human body is 60 percent water, which is lost continuously to perform bodily functions such as regulating body temperature and flushing out waste. Not drinking enough water to replenish your body’s water supply will severely impair your concentration.

Skin Dehydration
Dry skin is one of the obvious ways to tell if you’re experiencing dehydration. Some of the first warning signs of this condition include persistent dry skin, chapped lips, dry eyes, and dandruff.
As the largest body organ, the skin needs to be adequately hydrated at all times to perform its function and retain its appearance and texture. Otherwise, it becomes dry, which eventually leads to full-blown dehydration, a more severe condition. When the skin lacks water, it cannot produce sweat to wash off accumulated dirt and oil, causing various skill complications. To manage breakouts, drinking enough water should be your course of action.
Hunger after Eating
Dehydration can confuse your body into thinking it needs food when it just needs to rehydrate. Hunger due to dehydration can happen either during the day or at night when you wake up craving that midnight snack. Rather than satisfying your appetite, eating makes your body heavier, whereas drinking water cleanses your system and provide you with the necessary electrolyte to perform other functions.
This confusion of feeling hungry instead of thirsty happens in the hypothalamus, the part of our brain responsible for controlling thirst and appetite. If you find yourself feeling hungry just after eating, it may be your hypothalamus going haywire. Instead of going for extra helpings, drink water and see if you’re still hungry.
Fatigue and Lethargic
Many factors attribute to Fatigue and lethargic, including insufficient sleep and insomnia. But if you experience tiredness and sluggishness even though you’re getting enough sleep, then it may be a sign that you’re dehydrated.
When you are dehydrated, your blood pressure drops, leading to a reduction in hydrated blood flow to the brain and other parts of the body. Since oxygen can’t circulate your body, you become tired, dizzy, or lightheaded.
Muscle Cramps and Joint Pains
Muscle cramps are a common symptom of electrolyte imbalances, which is due to body dehydration. When you fail to replenish the water lost to sweating, especially during an exercise routine, you end up with cramps. Quickly drink water and rest if you’re feeling dehydrated while working out.
The cartilage between your joints and spinal discs to function correctly needs to be continuously lubricated with water. When it lacks the necessary fluid, it loses its elasticity, responsible for aching, cracking joints.
Drinking enough water helps the joints to be a better shock absorber.
Bad Breath (Chronic Halitosis)
Dehydration can be the cause of that bad breath you have. When you’re dehydrated, your body won’t produce enough saliva, which gives the bacteria in your mouth the opportunity to grow, leading to bad breath. Water moistens and lubricates the mucus membranes in your mouth and throat, promoting saliva production.
While dehydration can easily be solved by drinking a glass of water, leaving it untreated can lead to a more serious problem. Thus, it is essential you drink enough water every day, and as soon you notice any of the listed symptoms.
(01/03/2025)by ViraLifes
More Information: N
Views: 1,449
How To Identify The Known Bruxism Causes
When building a foundation for a healthy body, people traditionally focus on exercise, nutritious foods and the occasional doctor visit. Although mouth health tends to get overlooked in the process, it can make a profound difference on how you feel in other aspects of life. More commonly known as teeth grinding, bruxism is one mouth malady that shouldn't go untreated.
Is it common for you to wake up in the morning with a sore jaw or a headache? Do you at times clench your teeth? Until you have a dental examination or experience pain, you may not know that you are a victim of a condition known as bruxism. Bruxism is the clenching, gritting or grinding of teeth. Many individuals do not know that they clench their teeth as they mainly do it when asleep. Bruxism usually takes place during the early hours of the night and can result to irregular sleep patterns. In some people grinding and clenching can be fairly audible, while other people tend not to make any sound hence they do not know that they suffer from teeth grinding until they are told by a dentist. Apart from causing discomfort, bruxism can destroy dental restorations.
Signs and Symptoms
Bruxism has many symptoms that are similar to those of other conditions. Consult your dentist if you're concerned about:

Diminished tooth enamel and increased tooth sensitivity.
Jaw soreness or tight jaw muscles.
Grinding of the teeth loud enough to wake up your partner.
Flat, loose or chipped teeth.
A headache that begins at your temples.
Sleep Issues
It isn't known for certain what gives way to bruxism, but both physical and psychological causes are often linked to teeth-grinding. Sleep issues are some of the most common. Snoring, sleep talking and even a sleep disorder such as sleep apnea can play a role in developing sleep bruxism. Sleep apnea is a unique condition that affects the breathing process; be sure to see your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.
Negative Emotions
Anger, anxiety, frustration and stress are four major reasons a person may grind their teeth as a coping method. The latter is the big one. Although professional counseling can make it easier for you to deal with stress, there are personal ways to manage it as well. Exercise releases endorphins that provide tremendous stress relief, whereas certain relaxation methods – such as listening to music, taking walks and even a warm bath – are similarly helpful. Work-related issues are frequently to blame, so be mindful of your workplace atmosphere and how you approach the tough aspects of your career.
Malocclusions
Bite and alignment issues with the upper or lower jaw are another common cause of grinding. Something as simple as braces or as extreme as jaw reconstruction are potential fixes, but always discuss this treatment with your dentist to ensure you take the right course of action to correct any malocclusions.
Lifestyle
Substance-based habits such as tobacco use, alcohol consumption and even too much caffeine can increase your risk of bruxism. Your medical professional can even recommend a friendly form of addiction treatment if need be. Keep in mind that age is also a factor, as bruxism is more common in children before they're teenagers.
Medications and Disorders
Bruxism causes have also been linked to side-effects from psychiatric medications and antidepressants, along with neurological conditions like Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease. Consult your doctor in these cases.
Prevention and Treatment
If you suspect you suffer from bruxism, start listing any symptoms and call attention to them at your next dental appointment. Your dental professional may want to perform a full examination to confirm any symptoms or signs for sure, and then determine the reasons they have occurred. In the interim, he or she may prescribe a mouth guard to relieve any damage already done from grinding, or perform a dental procedure to correct any problems related to tooth alignment. Discussing stress reduction methods is another option if you haven't undertaken them.
As always, oral care starts at home.
(01/02/2025)by Colgate
More Information: N
Views: 578
What Does a Cavity Feel Like?
Cavities are pretty common. As the National Institutes of Health points out, the only condition more common than a cavity is the common cold. If you've never experienced tooth decay, you might wonder, "What does a cavity feel like?" The answer depends on the stage of the cavity and what foods you eat. Some foods, such as sweets, might trigger the pain of a cavity more than others.
How Cavities Form
Your mouth is naturally full of germs. Some of those germs are perfectly healthy, but others can be harmful. When you eat something sugary, such as candy or even potato chips, or drink a sugary beverage, the germs feed on the sugars in the substance. This produces acid, which is strong enough to wear away tooth enamel if not cleaned off quickly enough. In the end, a dental cavity begins to form.
In the early stages, a cavity can be reversed, as the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research notes. Brushing your teeth with a toothpaste that contains fluoride can help restore the enamel and reverse the effects of cavities.

Signs of a Cavity
What does a cavity feel like? In the earliest stages, the answer might be nothing. There are no nerves in your tooth enamel, so when the decay is in that layer, you likely won't feel a thing. Once the decay has progressed enough to reach the softer tissues inside the tooth, where the dentin and nerves are, you might notice signs of a cavity. Your teeth might feel sensitive and you could feel some pain, especially after eating sweets, hot foods or cold foods. The pain can be fairly mild or sharp and intense. Some people with cavities also feel pain when biting down.
Depending on the size of the cavity, you may be able to see evidence of it in your mouth. Cavities sometimes create visible holes in the teeth. They can also create stains that are black, brown or white on the surface of the tooth.
Cavities and Sweets
Why are you more likely to feel pain from a cavity when you eat sweets? Some foods, including sweets, are more likely to cause pain when there is enamel erosion. Sweet foods tend to be sticky, so they often cling to your teeth. The germs that feed on them can then produce more acid, which can make its way into the cavity, irritating the nerves. Even if you don't have a cavity, sugary foods will cause more sensation in sensitive teeth.
Seeing Your Dentist
What should you do if you think you have a cavity? The first step is to see your dentist. Although cavities can be reversed in the early stages, by the time you are feeling discomfort or pain, only a dentist can treat them. An x-ray will be taken to determine how the cavity has progressed into the tooth. Depending on how severe the cavity is, you might need a filling to fix it. If the decay is very severe, the dentist might replace the tooth with a crown or perform a root canal.
Even if you're not sure if you have a cavity, regular professional cleaning and dental visits are important. A dental hygienist can apply a fluoride treatment to help strengthen the teeth and reverse the very early stages of decay. He or she can also give you tips on the best ways to brush your teeth and advise you about what foods to avoid or consume less frequently to reduce your risk for cavities. As with many conditions, when it comes to cavities, taking preventative steps is a lot easier than treating the problem down the road.
(01/02/2025)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/cavities/what-does-a-cavity-feel-like
Views: 594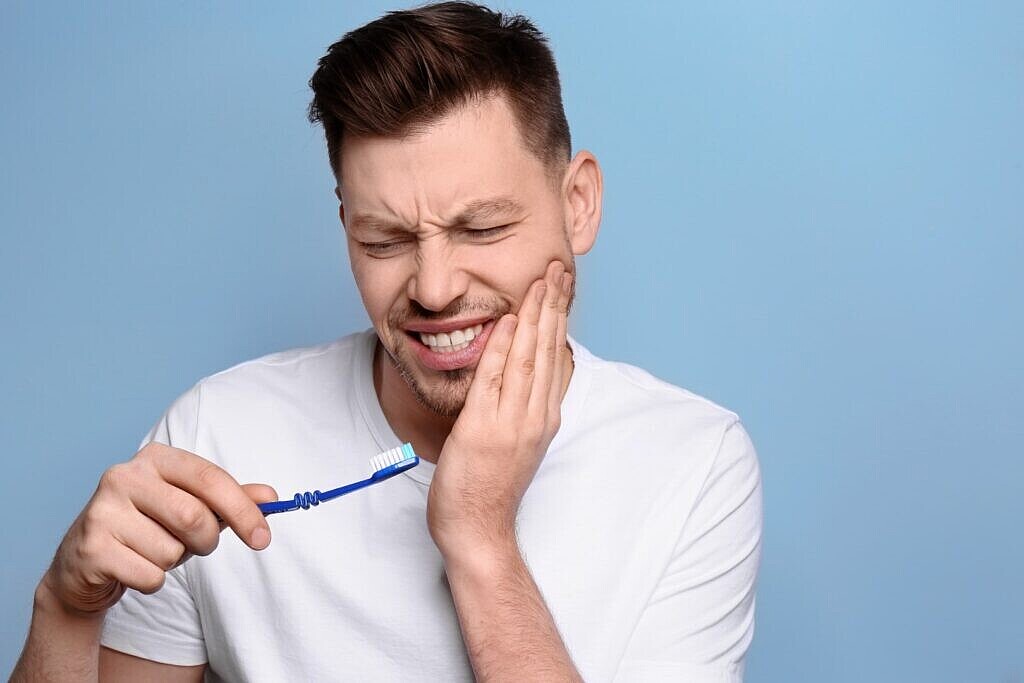
Possible Causes of Tooth Pain After Brushing
Have you noticed discomfort or pain after brushing your teeth? Picking up on warning signs of oral health issues and quickly acting on them is a great way to keep your teeth and gums in excellent condition. Read on for the top three causes of tooth pain and what to do about them.
Tooth Sensitivity
Cleaning your teeth is essential for keeping your smile healthy. If your teeth hurt after brushing or eating hot or cold foods, you may have tooth sensitivity. According to the American Dental Association, tooth decay and gum disease can cause tooth sensitivity, and you will need professional treatment. Your dental professionals can check for signs of oral health problems and recommend a treatment for tooth sensitivity, such as a special toothpaste, a crown, or an in-office application of fluoride gel.
Tooth sensitivity may be temporary. Some people report tooth pain shortly after a visit to their dental hygienist, if the dental hygienist has done any scaling or tartar removal. Your teeth could also be sensitive if you have gum recession, as the exposed root surface may cause discomfort. In this case, tooth sensitivity is likely only temporary, so you can simply brush your teeth with sensitive toothpaste. Usually, your teeth will return to normal within a few weeks. If they do not, call your dentist and ask them to check your teeth.

If a recent dental treatment is not to blame, food sensitivity can often be a side effect of damaged enamel, which you can't get back once worn away. Damaged enamel occurs when the hard mineral that protects your teeth's surface erodes over time, as explained by the United States National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR). Enamel erosion is usually the result of exposure to acid or excess sugar. Enamel that wears away can result in cavities and pain after brushing or flossing. If you suspect this is the reason for your teeth hurting after flossing or brushing, talk to your dentist.
If the enamel wears away to the point of exposing the sensitive nerves in your teeth, you have a cavity. These cavities often manifest as sharp pain when you bite down on something hard, and it doesn't have to be hot or cold to set you off. Cavities are small fissures in your teeth, but they can lead to more complicated problems if left unfilled. You should see your dentist as soon as you suspect you have one; he or she can fill it to prevent the condition from worsening.
Gum Problems and Cavities
Gum problems precede gum disease. Plaque build-up irritates gum tissue, making gums swollen and tender. Maintain proper oral hygiene and see your dentist if you notice these symptoms. As gum problems progress, they can become more challenging to treat.

The Wrong Toothbrush
If you notice pain and discomfort after brushing with a hard-bristled brush, it may be time to get a new toothbrush. Most dentists recommend a soft-bristled toothbrush to keep teeth clean. Good brushing technique with a soft brush can help remove plaque and help fight tooth cavities and gum problems without irritating your gums and teeth. Brush for two minutes using short, gentle strokes. Clean all the surfaces of your teeth, including the outside, inside, and chewing surface of those hard-to-reach back teeth.
As you can see, tooth pain after brushing may be a temporary inconvenience after a professional dental treatment, or it may be a sign of a more serious oral health condition. Maintain good oral hygiene habits with a soft-bristled toothbrush. Be sure to see your dentist if you notice pain, discomfort, or sensitive gums.
(12/30/2024)by Colgate
More Information: N
Views: 635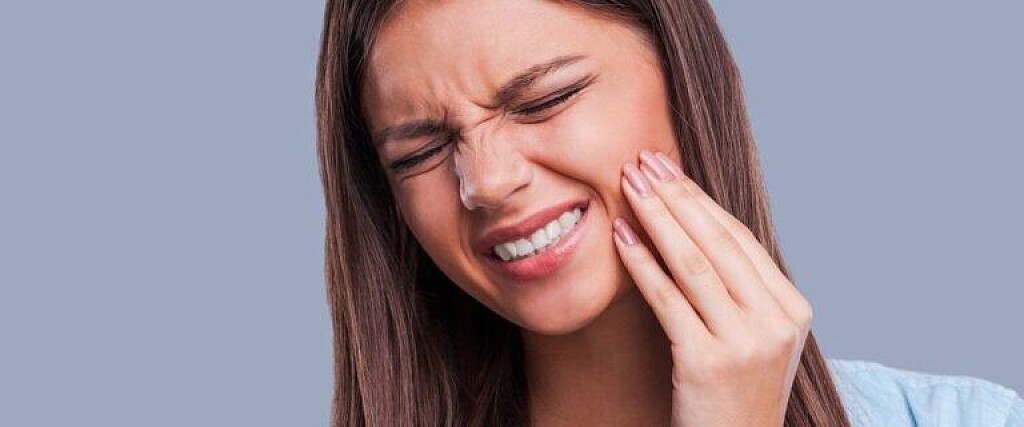
What Are the Dangers of Not Removing Wisdom Teeth?
Any type of surgery is scary, and it is natural for people wanting to postpone the surgery as long as possible. Similar is the case with a dental procedure, it can be daunting too. You might be postponing due to various reasons – as you will have to encounter wisdom teeth removal cost, you might have to avail a day’s leave for the procedure, and above all you are frightened!
But, this delay can be really dangerous and can have serious consequences on your health. Here are a few reasons as to why delaying the wisdom teeth removal can be a bad idea:
Wisdom teeth promotes Gum Disease
It is a challenging task to clean the area in which the third molars have erupted. Therefore they are at a greater risk of acquiring the periodontal problems. The gum diseases are usually caused by bacteria, and when a tooth can’t be precisely cleaned on a regular basis, the dental plaque gets accumulated around the tooth, which may lead to further complications.
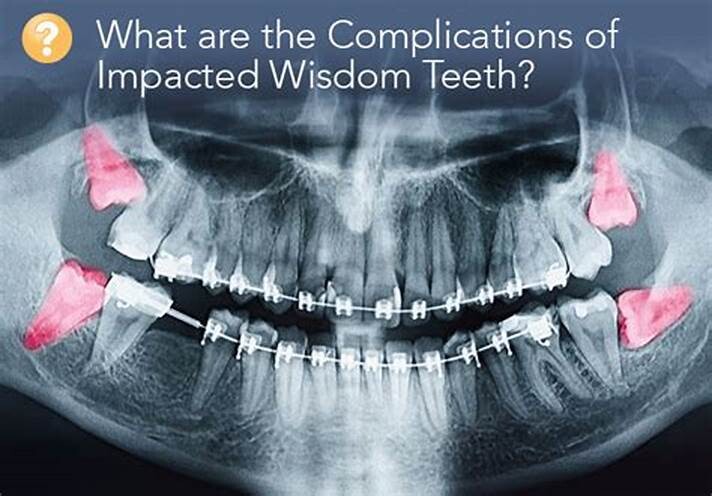
Formation of Cysts or Tumours
If the wisdom teeth problems are not dealt in an appropriate manner, the tooth will develop a sac within the jawbone. This sac has the ability to fill with fluid, which gradually develops into the formation of cyst, damaging the teeth, jawbone, and nerves. There are chances that this cyst could progressively develop into a tumour if untreated which could ultimately result in the removal of tissue and jaw bones.
Mutilates the Neighbouring Teeth
Since there is not enough room for the tooth to grow, it will case the teeth to grow in an abnormal manner. This results in impaction of the teeth, giving rise to many other oral problems. When the wisdom tooth emerges against the second set of molar, it might damage them, increasing the risk of acute infection. It will also have an effect on other teeth, which will intensify the need for an orthodontic treatment to align the other teeth.
Tooth Decay
The fully impacted or the partially impacted wisdom teeth are at greater risk of tooth decay, than other teeth. This usually happens, because of the location of the wisdom tooth, especially towards the back of the mouth, which is hard to clean. Moreover, since it lies at the back of the mouth, there are chances of food getting easily trapped between the gums and the tooth, promoting the growth of bacteria.
You can’t prevent the occurrence of an impacted wisdom tooth, but with a regular dental check-up, your dentist will help you monitor the emergence of the wisdom tooth, with the help of dental X-rays and advanced methodologies, which might indicate the need of wisdom teeth removal.
(12/30/2024)by Wisdom Teeth Day Surgery
More Information: https://wisdomteethsydney.com.au/what-are-the-dangers-of-not-removing-wisdom-teeth/
Views: 672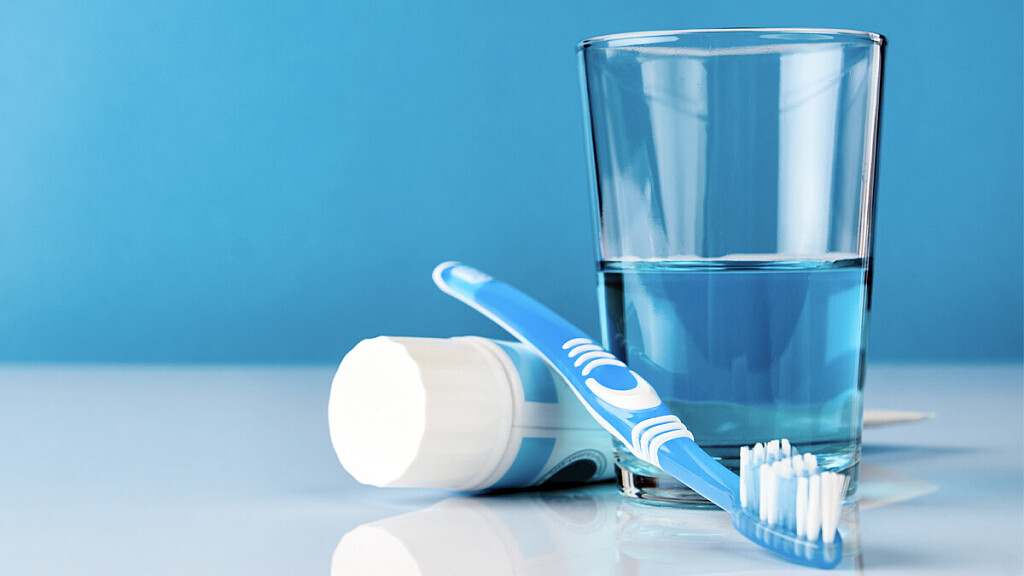
Should You Use Mouthwash Before or After Brushing?
Brushing and flossing are the foundations of a good oral hygiene routine‚ but mouthwash can also be a useful addition, thanks to the many oral health benefits it has to offer. If you've recently started using mouthwash, you may be wondering how you should incorporate it into your routine. Is it better to use mouthwash before or after brushing? And what else can you do to boost your oral health?
Benefits of Mouthwash
Mouthwash is probably best known for freshening your breath, but adding it to your daily oral care routine can provide many other benefits, too.
The South African Dental Association (SADA) recommends that you protect your mouth while on the go and after meals and snacks by rinsing with a fluoride mouthwash; this will freshen your breath and help guard against cavities. As the American Academy of Periodontology notes, untreated gum disease can lead to complications such as gum recession and tooth loss, but using mouthwash can help boost your prevention efforts.

Mouthwash achieves these oral health benefits by helping to control plaque, which is a thin film of germs that builds up on your teeth. When plaque isn't removed, it eventually hardens into tartar. The American Dental Association (ADA) reports that mouthwash can actually slow down the formation of tartar, too.
When to Use Mouthwash
When you first add mouthwash to your oral care routine, you may wonder: Should you use mouthwash before or after brushing? This is a good question, and it doesn't have a simple answer. The scientific research is limited, and reputable organisations offer different recommendations.
The US-based Mayo Clinic recommends using mouthwash after brushing and flossing your teeth. However, the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom recommends avoiding mouthwash right after brushing, since this may wash away the fluoride from your toothpaste. Instead, the NHS recommends using mouthwash at a different time of day.

The ADA states that you can use mouthwash either before or after brushing, depending on your personal preference. That said, mouthwash manufacturers may recommend an order based on their product's ingredients, so check the label on your product to ensure that you maximise its effects.
Other Ways to Boost Your Oral Care Routine
Mouthwash may enhance your oral care routine, but remember: it's not a substitute for regular brushing and flossing. Brush your teeth twice a day for at least two minutes to remove food particles and plaque from your teeth, and floss once a day to clean between your teeth and along your gumline.
If you want to make further improvements to your daily oral care routine, consider these tips from the South African Dental Association (SADA):
Eat a well-balanced, tooth-healthy diet
Limit high-sugar foods and drinks, such as sweets and fizzy drinks
Avoid frequent snacking
Apply toothpaste to the full length of your toothbrush head
See your dentist regularly for check-ups.
While it's not a replacement for brushing and flossing, mouthwash can play an important role in your oral hygiene routine. It can help to freshen your breath, remove plaque and reduce your risk of cavities and gum problems. For help deciding whether to use mouthwash before or after brushing, talk to your dentist.
(12/28/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/brushing-and-flossing/should-you-use-mouthwash-before-or-after-brushing
Views: 662
Five Signs It’s Time To See An Orthodontist
Abright, even smile is truly a sight to behold. It not only lights up a face but also instills confidence and self-assurance. Orthodontics is a specialized discipline of dentistry that offers comprehensive treatments for diagnosing, treating, and repairing anomalies in teeth and jaw alignment. Orthodontic treatments are essential in correcting functional issues that can significantly impact oral health.
If you have teeth/jaw irregularities, you should consult with an experienced orthodontist in your vicinity before it evolves into a serious problem—particularly if you reside in the state of Connecticut, where over 164 million work hours are lost every year due to dental health issues. And if you’re located in a city like Glastonbury, finding a reputable orthodontist is as simple as a few taps on your smartphone screen.
In this blog, we’ll explore five signs indicating it’s time to see a good orthodontist. So, let’s get started!
Crowded or Crooked Teeth:

Overcrowded or crooked teeth are one of the most obvious signs that you should see an orthodontist. An overcrowded mouth usually results from insufficient room for a full set of teeth in the mouth, among other reasons.
Fortunately, you can get orthodontic treatment in Glastonbury, CT, to remedy this issue. An orthodontist can evaluate your specific case and develop the appropriate treatment plan. Braces or aligners are popular options that gradually shift teeth into their correct position, aligning your smile with the breathtaking splendor of Glastonbury itself.
Crowded teeth not only detract from a smile’s appearance but also endanger dental health. Misaligned teeth can be twisted, slanted, or overlapping, creating hiding places for plaque and germs that, if not corrected, can lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
Overbite Or Underbite:
An overbite or underbite is more than just a dental misalignment; it can substantially impact a person’s everyday life, affecting everything from how they eat and speak to how their jaw functions. An overbite or underbite throws off the balance of life, making orthodontic treatment necessary.
An overbite occurs when the upper front teeth completely cover the lower front teeth, causing discomfort and impairing speech clarity. Conversely, an underbite occurs when the lower teeth protrude beyond the top teeth, causing biting difficulty and potential jaw strain.
Orthodontic treatment provides a light of hope for people who have overbites or underbites. Extensive evaluation of each individual’s unique dental condition by experienced orthodontists results in done and personalized treatment plans. It’s designed to remedy these bite irregularities. They straighten the teeth and jaw using treatments such as braces or aligners, relieving discomfort and preventing long-term issues such as jaw pain and excessive tooth wear.
Beyond aesthetics, treating overbites and underbites is essential for ensuring healthy dental function. A balanced bite boosts not only their confidence but also their capacity to enjoy meals and communicate successfully.
Early and Late Loss of Baby Teeth:
Early or late tooth loss can significantly impact a child’s dental development, laying the groundwork for potential oral health problems. Each child’s path to a brilliant smile is unique, and understanding the significance of tooth eruption can help parents and caretakers protect their children’s oral health.
Early tooth loss, frequently linked to dental decay or trauma, can interrupt the normal order of tooth eruption. When baby teeth are lost prematurely, neighboring teeth may wander into the empty gap, preventing permanent teeth from effectively aligning. This misalignment might cause biting difficulties, including tooth crowding or gaps, which may demand future orthodontic correction.
Late loss of baby teeth can be concerning. If baby teeth are present for an extended time, it may signal an underlying issue, such as impacted permanent teeth or developmental difficulties. Early detection and treatment of these abnormalities can help prevent potential difficulties and guide the child’s oral growth in the appropriate path.
Regular dental check-ups and consultations with orthodontic professionals ensure that any issues are treated immediately. Orthodontists can apply measures to assist appropriate tooth eruption and jaw growth, laying the groundwork for a healthy bite and a beautiful smile.
Difficulty In Chewing Or Biting:
The process of chewing and biting may appear monotonous, but it is essential in our daily life. When difficulties emerge during this seemingly effortless action, it may indicate underlying dental disorders that must be addressed. Both adults and children can have problems breaking down food, and recognizing these signals is critical for their well-being.
Misaligned teeth or jaw problems might make it difficult for our dental system to work properly. Their ramifications can be far-reaching. Chewing or biting difficulties can lead to inefficient food breakdown, compromising digestion and nutritional absorption. This might lead to malnutrition and other health difficulties, emphasizing the importance of addressing such issues as soon as possible.
An orthodontist is essential in identifying and addressing these issues. Their knowledge of tooth and jaw alignment allows them to precisely diagnose the root cause of the problem. After a comprehensive evaluation, they can provide appropriate treatment solutions to improve oral function. Orthodontic treatments, whether braces, aligners, or other products, can straighten teeth and jaws, allowing for more effective chewing and biting and averting future health problems.
The impact of these challenges extends beyond physical health to include mental well-being. The irritation of being unable to eat comfortably can harm a person’s self-esteem and confidence. Individuals can reclaim their dental function and sense of self-assurance and joy by obtaining orthodontic care.
Wear and Tear of Teeth:
The unrelenting grind of our daily life can occur in unexpected ways, including harming our teeth. Bruxism, or grinding or clenching one’s teeth, may appear inconsequential initially, but the effects can be severe. This persistent movement can cause excessive wear on tooth surfaces over time, resulting in worrying symptoms such as shorter or chipped teeth, increased sensitivity, and jaw pain.
The emotional impact of watching our smiles deteriorate cannot be overstated. Each chip on a once-perfect tooth may show our tension and anxiety. The story, however, does not end there. Armed with dental health skills, an orthodontist can act as a guardian, guiding us back to the right road.
Orthodontists can combat the consequences of bruxism with personalized treatment strategies. Tailored solutions seek to reduce tooth wear and tear while relieving sensitivity and jaw pain. Orthodontic care, addressing the underlying cause, not only restores the appearance of our teeth but also ensures long-term protection against additional damage.
(12/28/2024)by Today's Woman, Articles, Product Reviews and Giveaways
More Information: N
Views: 608
Root Canals: Three Signs You May Need One
Curious about root canals? Read on to learn more about when this procedure is recommended. Regular dental checkups are essential components of maintaining oral health. Although some teeth that need root canals may not cause symptoms, in most cases, patients will experience signs that are hard to ignore. Generally, when experiencing dental pain that disrupts sleep, work, or leisure, it is time to consult a dentist.
3 reasons that root canals may be recommended
A root canal is a procedure aimed at cleaning out tooth roots and sealing the space with a biocompatible material. After a root canal, the dental professional places a permanent restoration such as a dental crown. Undertaking these steps helps save teeth that might otherwise require extraction.
Here are three common signs that one may need a root canal:
1. Tooth pain
While tooth pain does not always indicate a need for a root canal, it does signal an issue. A thorough examination by a dentist can help determine the cause. Dental pain can range from mild to excruciating and may be constant or intermittent. Patients might feel pain only when chewing, or it could persist for hours or days. Pain often changes in intensity over time.
Root canal pain typically starts with mild discomfort, progressing to extreme pain or sensitivity, and may eventually lead to an abscess or infection if left untreated.
2. Swelling

Swelling can vary from mild to severe. Patients may notice a tender, slightly raised spot on the gum near the tooth, or experience swelling in their neck or face. This area may or may not drain fluid and is likely to feel sore or tender. Long-standing dental issues can cause swelling that recurs over weeks, months, or years. Regardless, swelling is a clear sign of a problem requiring immediate attention, so consult a dentist immediately.
3. Temperature sensitivity
Dentin hypersensitivity, or sensitive teeth, can have various causes. However, a new sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures can sometimes be the only outward indication that a tooth needs a root canal. Patients might feel mild discomfort, and consuming hot or cold items like cold water or hot pizza could be unbearable. The dentist will determine the source of the pain and whether a root canal is necessary.
The symptoms above often manifest when a tooth grapples with a severe infection. Unfortunately, by the time patients experience pain, heightened sensitivity, or detect an abscess, the bacteria have already infiltrated the inner pulp of the tooth. The dentist can identify potential problem areas through X-rays during routine dental cleanings and exams. Even a minuscule crack or chip in the tooth can be an open invitation for bacteria to enter its inner canal.
(12/27/2024)by Dental Partners Fountain City
More Information: N
Views: 581
Signs A Broken Tooth Is An Emergency
A broken tooth does not always count as a dental emergency unless it requires immediate dental care. A broken tooth can be the result of biting into something too hard, especially if the tooth has already been weakened by tooth decay. It can also be caused by trauma to the face or habits like teeth grinding.
A broken tooth ruins the aesthetic of your smile, and it can affect your ability to chew. A broken tooth is also more vulnerable to decay because food particles and other debris will build up when the tooth is broken. Fortunately, dentists have several tools at their disposal when it comes to treating broken teeth, like dental crowns.
How to determine if a broken tooth requires emergency care
Not sure if your broken tooth counts as a dental emergency? Here are a few things that you should be look for.
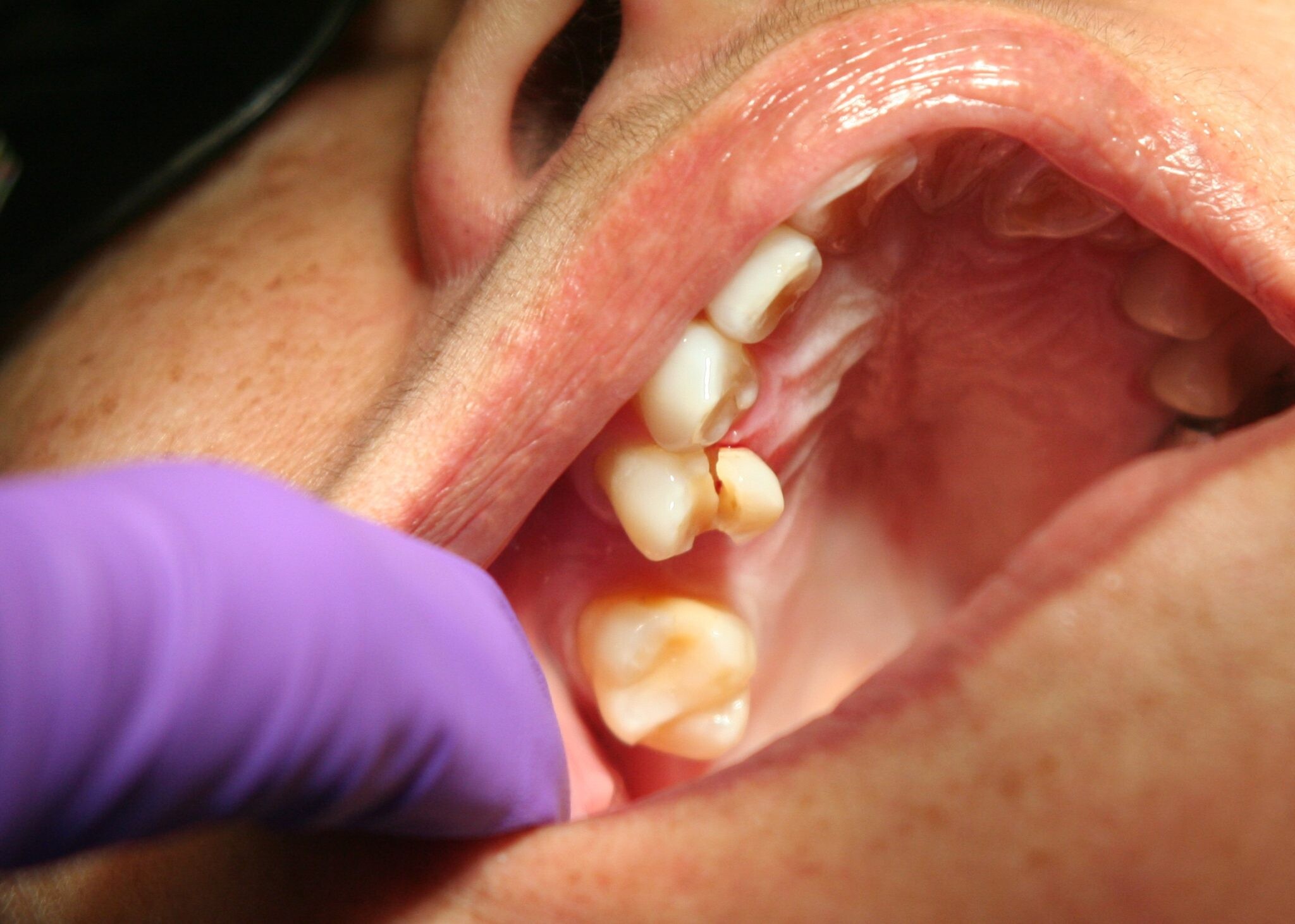
1. Excessive bleeding
Excess blood coming from a broken tooth is usually a sign that the tooth has serious internal damage. In many cases, the tooth’s pulp chamber has been compromised, leaving the nerves and blood vessels in there exposed to irritants in the mouth, like bacteria and acids.
Such injuries are often accompanied by excruciating toothaches, increasing the need for urgent treatment. Severe damage to a tooth is often addressed by performing root canal therapy. During the procedure, the dentist removes the soft tissues in the pulp chamber and disinfects the area. The tooth is sealed back up and covered with a crown to provide additional protection.
2. Loose tooth

A broken tooth that is loose because of an injury requires emergency care. If left untreated, the tooth can end up falling out. Dentists can easily address a loose tooth by securing it to other stable teeth with a splint. This keeps it firmly in place in the patient’s mouth, allowing its roots to form new bonds with bone tissues around them. The dentist can then perform appropriate treatments for the broken tooth, like composite bonding or a crown.
3. Excruciating toothaches
Dental issues that cause a person unbearable pain are usually classified as dental emergencies. Standard dental appointments involve waiting for one or more weeks to see a dentist. People who are dealing with intense pain require immediate access to a dentist.
Intense pain coming from a broken tooth is typically a sign that the tooth’s pulp chamber has been damaged. This leaves the nerves and blood vessels in there exposed to acids and bacteria. It is these irritants getting into the pulp chamber that leads to pain.
A dentist can resolve these by performing a root canal to remove the nerve and blood vessels. The tooth is then sealed up and covered with a dental crown.
(12/27/2024)by Dental Partners Fountain City
More Information: N
Views: 589
Prophylaxis Teeth Cleaning
Regularly scheduled dental cleanings are crucial in keeping your teeth and gums healthy.
A prophylaxis treatment is a technical term for regular teeth cleaning. Prophylaxis appointments and proper at-home oral care can contribute to a radiant smile and overall well-being.
This article explores what dental cleaning entails, and what you can expect during a prophylaxis session.
Prophylaxis dental cleaning, is a preventive dental procedure to remove plaque, tartar, and stains from the teeth and gums.
Prophylaxis dental cleaning is an essential part of maintaining optimal oral health.
This procedure is typically performed by a dental hygienist or a dentist in a dental office.
Is Prophylaxis the Same as Teeth Cleaning?
Yes, prophylaxis is a dental term for regular teeth cleaning and involves the removal of plaque and tartar.
Dental scaling and root planing is a more intensive procedure to treat gum disease. It involves cleaning below the gum line and smoothing the tooth roots to eliminate bacteria and promote gum healing.
On the other hand, regular dental cleaning is a preventive measure that focuses on maintaining oral health and preventing the progression of gum disease.
It is generally recommended for individuals with healthy gums and serves as a routine cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
What is Done During a Dental Prophylaxis Session?
A dental prophylaxis session usually involves several steps to ensure thorough cleaning of your teeth and gums.
During a teeth cleaning appointment, you can expect the following procedures:
Examination: The dental professional will comprehensively examine your mouth before the cleaning begins. This examination helps identify oral health issues and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Plaque and Tartar Removal: Using specialized dental instruments, the dental hygienist or dentist will carefully remove plaque and tartar deposits from your teeth. They will focus on areas that are hard to reach during regular brushing and flossing.
Teeth Polishing: After plaque and tartar removal, the dental professional will polish your teeth using a rotating brush or a rubber cup with an abrasive paste. This step helps remove surface stains and leaves your teeth looking clean and shiny.
Flossing and Rinsing: Once the teeth are polished, they will floss between your teeth to remove any remaining debris or plaque. They may also ask you to rinse your mouth to remove any residual polishing paste or debris.
Oral Health Education: To promote good oral hygiene practices, they may provide personalized tips on brushing techniques, flossing methods, and other oral care measures. They may also recommend specific dental products tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
By removing plaque, tartar, and stains, this preventive procedure helps prevent gum disease and other oral health issues.
Remember to consult your dentist regularly to determine the appropriate type and frequency of dental cleanings based on your unique oral health needs.
(12/26/2024)by Noble Dental Care
More Information: https://nobledentalcare.com/prophylaxis-dental-cleaning/
Views: 625
What’s the Difference Between Tartar and Plaque?
Understanding oral health can sometimes feel like navigating a maze of medical terms. Two such terms that are often confused are tartar and plaque. Dr. James Sunners, a renowned dentist with years of experience, explains the differences between tartar and plaque and why knowing these differences is essential for maintaining optimal dental health.
Understanding Plaque: The Primary Culprit
Plaque is a soft, sticky film that builds up on your teeth and gums. It’s primarily composed of bacteria, along with food particles and saliva. Plaque forms continuously and is the leading cause of various dental problems, including cavities and gum disease.
Key Characteristics of Plaque

Color and Texture: Plaque is colorless or pale yellow and has a sticky, slimy texture.
Formation: It forms constantly on your teeth, especially in hard-to-clean areas.
Control: Regular brushing and flossing can effectively remove plaque.
The Risks of Ignoring Plaque
If plaque is not removed regularly:
Tooth Decay: The acids plaque bacteria produce can erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
Gum Disease: Plaque buildup along the gum line can cause gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums.
Transitioning to Tartar: When Plaque Hardens
Tartar, or dental calculus, is what plaque becomes when it hardens on your teeth—Tartar forms when plaque is left undisturbed on the teeth and reacts with minerals in your saliva.
Characteristics of Tartar
Hardness: Tartar is a complex, crusty deposit that can only be removed by a dental professional.
Visibility: Unlike plaque, tartar can be easily seen. It often appears as a yellow or brownish deposit along the gum line or between teeth.
Why Tartar is a Concern
Tartar buildup:
Promotes Decay: Creates a rough surface that facilitates more plaque accumulation, leading to increased tooth decay.
Gum Problems: This can lead to more severe forms of gum disease like periodontitis.
Prevention and Removal of Plaque and Tartar
The key to preventing tartar is controlling plaque. Dr. James Sunners recommends the following:
Regular Brushing: Brushing your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste. Pay special attention to the gum line, where plaque tends to accumulate.
Flossing Daily: Flossing removes plaque between teeth and under the gumline, areas where a toothbrush can’t reach.
Dietary Choices: Limit sugary and starchy foods that feed the bacteria in plaque.
Regular Dental Checkups: Regular visits to the dentist, like Dr. James Sunners, allow for professional cleaning to remove tartar and any plaque you may have missed.
(12/26/2024)by James R. Sunners D.D.S.. P.C
More Information: https://sunnersdds.com/whats-the-difference-between-tartar-and-plaque/
Views: 635
How Long Does A Tooth Extraction Take To Heal?
Within this blog we will be covering all the key points to know about how long a tooth extraction takes to heal. This includes the time & stages of tooth extraction, how to speed up healing, and whether you extraction is healing correctly.
Tooth Extraction Healing Time and Stages
The time a tooth extraction takes to fully heal will largely depend on where the tooth was located, and the type of extraction that was performed. Typically, the healing time is between 7-10 days, although in more serious cases it is possible for healing to take between 2-3 weeks. The key stages of tooth extraction healing have been outlined below.
Stage One: This first stage comprises the initial 24 hours directly after the extraction and includes the formation of a robust blood clot. It is likely that there will be some discomfort, inflammation, and potentially light bleeding during this stage.
Stage Two: This stage involves the next 24 hours after stage one, and at this point the clot begins to properly form around the socket area. At this point the platelets within the clot have started to produce chemical factors which will encourage healing, while inflammation will begin to decrease.
Stage Three: By 3-4 days, this stage begins, and it will involve the early closure of the gum tissue around the extraction site.
Stage Four: This is the final stage, and it takes place around 4-7 days after stage three and 7-10 days after the initial extraction has taken place. At this point the extraction site has effectively fully healed, although it is possible that some extra time is needed in complex extraction procedures.
Speeding Up Healing
As mentioned before the healing process will vary based on where the extraction took place and the complexity of the extraction itself, although some tips to ensure the healing occurs swiftly have been detailed below.
Immediately following the procedure, you can ice the area to minimise pain or swelling for around 15 minutes, and should wait around 15 minute intervals in between future ice pack use
You should bite down on the gauze for 5-15 minutes after the procedure to ensure pressure is being applied sufficiently, and this should be repeated if it starts to bleed again.
Once the first 24 hours after the extraction have passed then you can begin to use a warm saltwater rinse. This involves a teaspoon of salt and a glass of warm water and can be used daily.
Any pain relief medication that has been given by the dentist should be taken as prescribed, otherwise you are able to purchase you own medication. However, check first with your dentist/doctor to ensure they won’t be problematic for the healing process.
Is the Extraction Healing Correctly
In many scenarios patients who have teeth extracted are unaware if their affected area is actually healing in the correct manner. You will be able to tell if it is healing correctly, if the first few days only involve some light bleeding, inflammation, and minor discomfort. Additionally, if you see some bruising around the area or stiffness in the jaw then this is perfectly normal. There may also be some small fragments of tooth/ root within the socket or sharp edge of the bony socket, which often clear and self-resolve. Help should only be sought if they don’t come out by themselves.
You will know that the extraction is healing correctly if there are noticeable improvements as the days pass by. You may even take pictures to monitor this and compare them will extraction healing pictures available online, to ensure that everything is normal. If you believe that your healing process is not occurring correctly then you should contact your dentist immediately. While in the majority of cases there is no issues, it will help put your mind at ease.
(12/23/2024)by The Denture & Implant Clinic
More Information: N
Views: 776
What To Do If Your Teeth Are Crumbling?
If your teeth are crumbling or if a piece of a tooth suddenly breaks off, it’s essential to visit a dentist promptly. Doing so increases the likelihood of fully restoring the damaged tooth without resorting to radical methods.
Here are if your teeth are crumbling:
Reasons Why Teeth Can Crumble
There are various reasons why teeth break, and only a dentist can accurately determine them. Here are some common causes of tooth decay:
injury by hard foods – if you peel pistachios with your teeth or accidentally bite into hard popcorn, it can lead to a tooth fracture and its further destruction;
caries – a pathological process that slowly and initially imperceptibly destroys tooth enamel, which eventually causes the tooth to crumble or break;
consumption of sour and sweet foods – the abuse of such products negatively affects the condition of tooth enamel, which gradually becomes thinner, less durable and unable to fully protect teeth;
bruxism – teeth grinding is harmful to dental health, as it leads to the destruction of enamel and causes tooth fragility;
insufficient oral hygiene – neglecting regular brushing, refusing to use dental floss and mouthwash can lead to caries and, consequently, to brittle teeth;
old age – with age, calcium reserves in the body are depleted, which can cause teeth, which are almost 95% composed of this mineral, to begin to crumble.
In addition, teeth are crumbling as a result of an accidental sports or household injury or accident.
What symptoms precede tooth decay?
Caries is one of the most common causes of tooth decay. The main problem is that in the initial stages, caries develops almost imperceptibly. when certain symptoms appear, it can already damage the tooth quite severely. That is why it is important to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist twice a year.
Here are the symptoms that can precede tooth decay:
the shape of the tooth changes – defects, cracks or chips appear on the enamel;
the enamel softens, becomes rough, yellow or brown spots may be visible
increased tooth sensitivity, pain when chewing food, under the influence of hot or cold drinks, sweet or sour food, etc.
In case of such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. A timely visit to the dentist will minimize the consequences.
What to do if a tooth is broken?
First of all, you should make an appointment at the dental office Queens, where doctors have extensive experience in fixing such problems. If a tooth is broken off, you cannot do without a doctor’s intervention, because you cannot cope with it on your own. The dentist will conduct an examination, assess the severity of the situation, and explain all the stages of treatment and restoration of the damaged tooth.
Treatment of injured teeth at the VIP Dental Care Clinic is carried out using advanced technologies and international standards. The priority is always to preserve and restore the broken tooth, not to remove it.
Professional dentists at VIP Dental Care Clinic perform all types of treatment and restoration of the dentition. If the tooth cannot be restored, the patient will be offered the installation of veneers, pins, or prosthetics with artificial crowns. If the tooth is completely destroyed, the doctor will recommend considering bone augmentation and implantation.
The doctor’s task is not only to restore the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the dentition but also to eliminate the cause of the decayed tooth or teeth. This will help minimize the risk of such problems in the future.
Preventive measures to prevent tooth decay
If you have previously experienced tooth decay and have undergone appropriate treatment at the dental clinic, it is essential to take preventive measures to avoid the problem from recurring. To do this, you should:
Brush your teeth twice a day and use dental floss regularly.
Visit the dentist twice a year for professional cleanings and check-ups.
Limit the consumption of sweets and other unhealthy foods.
Include calcium-rich foods in your diet.
Avoid injuring your teeth by biting hard objects like seeds or nuts.
Consult a dentist if you have bruxism to discuss treatment options such as a mouth guard or medication.
If your teeth are crumbling, it’s crucial not to delay addressing this issue, as the consequences can be serious. While initial treatment is typically straightforward and affordable, significant decay or complete tooth loss may require multiple dental visits, and implantation is a costly procedure.
(12/23/2024)by The Enterprise World
More Information: https://theenterpriseworld.com/what-to-do-if-your-teeth-are-crumbling/
Views: 717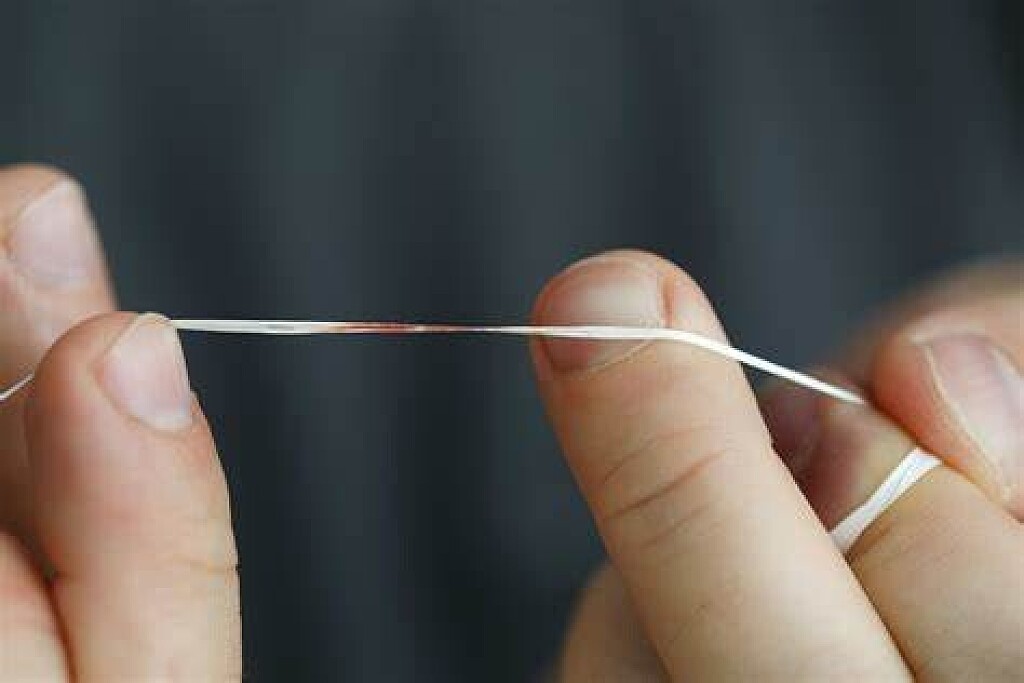
Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Floss?
Bleeding gums could mean you need to floss more often, or they might be a sign of a more serious problem.
Do your gums bleed when you floss your teeth? Gums can bleed for different reasons, but if they bleed regularly, or you have other possible warning signs of a problem, you should make an appointment with a dentist.
Your dentist will determine the reason why your gums are bleeding and discuss ways to stop the bleeding and address any underlying problems. Here are the common reasons why gums may bleed when flossing and how this may be prevented.
First-time or infrequent flossing
Bleeding gums are more likely to happen if you're not a regular flosser. When gums are not used to the sensation of flossing, they may feel itchy, sore or bleed in certain areas. This type of bleeding normally stops within a few minutes and should stop happening within the first week of a daily flossing routine.
If your dentist or hygienist thinks you might be flossing too roughly, or not enough, they will discuss your flossing method and demonstrate how to floss correctly. Flossing should be done at least once a day, before or after brushing.
To floss correctly using standard dental floss:
Pull off between 30cm and 45cm of floss and wind it around the middle fingers of both hands

Holding a length of floss between your thumbs and index fingers, gently slide it between two teeth
Gently clean up and down the sides of each tooth and tuck the floss slightly under the gum line
Move to a new section of floss and repeat for all of your teeth, discarding the floss after use
Trying a floss alternative
Improper flossing or brushing
If you are a regular flosser, bleeding gums could be a sign that you're flossing or brushing your teeth too roughly. Cleaning your teeth should be a gentle process, using soft floss and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Brushing and flossing harder doesn't remove more plaque, but it can lead to irritation, bleeding, or even permanent damage to gums and tooth enamel.
Toothbrush heads typically need replacing every 3 months, if you're replacing them sooner because of frayed bristles, it could be a sign that you're brushing too hard.
Gum disease
Bleeding gums are a common sign of gum disease (periodontal disease), especially if you have other symptoms such as inflamed, red or tender gums. Gum disease is caused by plaque and tartar that build up on the teeth around the gumline. It may be treated by improving your oral hygiene and seeing a dentist or hygienist for gum disease treatment.
Nutritional deficiencies
If your diet is low in vitamin C or vitamin K, you are more likely to have bleeding gums. Vitamin C helps to repair damaged gum tissue, while vitamin K helps with blood clotting. Both vitamins are also important for building healthy teeth and bones.
Hormonal changes
The influx of hormones during times such as pregnancy, puberty and menopause can result in bleeding gums for some women by increasing blood flow to the gums and affecting the body's immune response to bacteria in plaque. Bleeding gums have also been linked with stress.
Medical conditions and medications
Some underlying medical conditions may cause gums to bleed, including diabetes and autoimmune diseases. It may also be a side effect of certain medications, such as blood-thinning medications. Your dentist will check your medical history and may consult with your doctor to discuss treatment options.
Trauma or dental treatments
How to stop gums from bleeding when flossing
Not flossing because you're worried about bleeding gums can make underlying oral health problems worse. Flossing is an important part of daily oral care, as it cleans the surfaces between your teeth and around your gums that your toothbrush can't reach. If you don't floss, bacteria and leftover food can build up on these surfaces, leading to problems such as tooth decay and gum disease.
Bleeding gums when flossing can usually be prevented by improving your oral hygiene routine, lowering your risk factors for gum disease or treating an underlying problem. Your dentist will recommend which approaches are most appropriate for you.
Improving your flossing technique
If you find flossing uncomfortable or difficult, your dentist might recommend alternatives to traditional floss that can be gentler or easier to use. These include:
Dental tape – a thicker style of dental floss that is gentler on gums
Pre-threaded flosser – disposable floss holders that can make flossing easier for beginners
Interdental brush – fine brushes for cleaning between the teeth
Water flosser – a hand-held appliance that directs a jet of water at teeth
There are a few sustainable options on the market to help you reduce plastic waste, including reusable silicone floss and biodegradable floss made of bamboo, beeswax or silk.
Steer clear of metal floss and avoid using toothpicks or sharp objects to clean between your teeth or remove trapped food, as these can damage your teeth or gums.
Improving your oral hygiene
Besides flossing, regular toothbrushing is important for keeping plaque at bay and preventing gum disease. Toothbrushing should be done at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush.
If you have sensitive teeth or gums, your dentist may recommend using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth. They may also recommend a mouthwash if you need to reduce bacteria in your mouth.
Treating gum disease
If your dentist diagnoses gum disease, their treatment recommendations will depend on how far the disease has advanced.
Gingivitis is the mild form of gum disease and is usually reversible with good daily oral care and professional hygiene treatments at a dental clinic.
Periodontitis is the more severe form of gum disease that requires more intensive periodontal treatment. This can involve scaling and root planing to remove hardened plaque and tartar from under the gumline, removing infected pockets and treatments to restore lost gum or bone tissue.
(12/21/2024)by EVP Dental
More Information: N
Views: 679
Unlocking Three Benefits Of Brushing Teeth At Night
Like clockwork, we brush our teeth every morning to start the day with fresh breath and clean teeth. However, some of us get a bit lax about night brushing. What you may not realise is that this simple habit can save you a lot of dental health trouble.
Let's refresh our knowledge on the benefits of brushing teeth at night and how embracing this habit can reduce the chances of you getting a cavity by as much as 50%.
How important is it to brush your teeth at night?
Your oral health is an intricate part of your overall well-being. Throughout the day, your mouth encounters a variety of foods, each leaving behind particles and debris on your teeth. Some of these particles (such as sugary foods) are particularly notorious in sticking to your teeth and being attacked by germs.

A lot happens in your mouth while you sleep,
Germs are amongst fastest reproducing organisms in the world, hence by night time they have grown back by multifolds and are ready to act
Our Saliva flow rate drops to almost zero during night time which impacts the clearance of food debris and remineralisation of teeth
These overnight hours can become an opportunity for trouble. This makes night brushing a crucial part of your routine.

What happens if we skip brushing at night?
It can result in cavities and gum disease. When you go to bed without night brushing, the plaque in your mouth hardens. Once plaque hardens, it becomes tartar and is resistant to brushing. When left unchecked, cavities begin to form.
3 benefits of brushing teeth at night
1 . Reduces risk of cavities by 50%
One of the most significant advantages of night time brushing is its role in reducing the growth of harmful germs. Regular brushing before bed keeps germs in check and reduces the risk of cavities by 50%
2. Clears out food particles
Tiny particles from foods can get stuck in your mouth. Brushing at night using proper technique can help dislodge these particles and leave a clean mouth.
3. Can save you from painful treatments
Ignoring your oral hygiene can lead to significant problems down the road. From tooth removal to the dreaded root canal treatment, it can be both costly and time-consuming. Root canal treatment is a complex process that can be avoided by brushing morning and night everyday.
Improving Oral Health - Basic Tips To Take Care Before Bedtime
There are numerous ways to support your oral health while you seep.
Prioritize Night Brushing: Brushing your teeth before bedtime protects you from plaque buildup, tooth decay, and gum disease.
Improve Your Technique: Gentle, back-and-forth strokes are ideal for cleaning. Begin with the exterior surfaces of the teeth, then go on to the inner chewing areas. Use the brush's tip with gentle up-and-down strokes to clean the back side of your front teeth.
Address Teeth Grinding: If you wake up with teeth that are more sensitive or cuts on the inside of your cheek, it might mean you are grinding your teeth during sleep.
The best way to prevent teeth grinding, is to wear a special mouth guard while you sleep. This guard will shield your teeth from the harmful effects of grinding.
Take into account the benefits of brushing teeth at night and adopt this habit to ensure a healthier smile.
(12/21/2024)by Colgate
More Information: N
Views: 596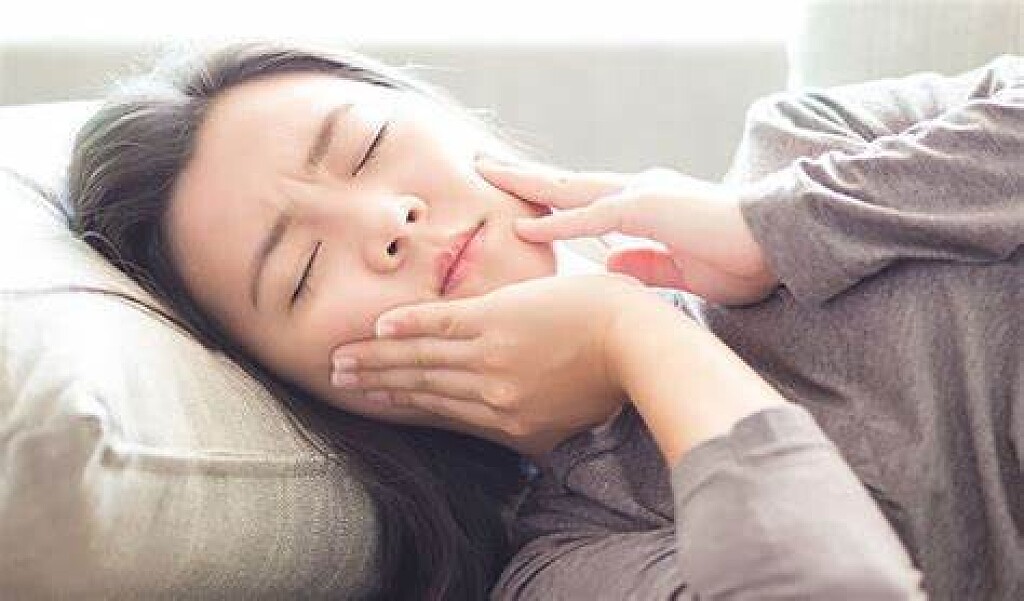
Reasons Why Your Toothache Hurts More at Night
Lack of Oral Hygiene
Your teeth and gums are the main channels into the body, so if you neglect oral hygiene, it may have a huge impact on your overall health. Tooth decay, gum disease, bad breath, oral abscesses, and even tooth loss are potential consequences of neglecting good oral hygiene. Therefore, it is necessary to brush your teeth before going to bed and pay attention to oral hygiene.

Less Distractions
At night, there are fewer distractions than during the day, making it likely that your toothache will hurt more when trying to go to sleep.Increased Blood Circulation

Increased Blood Circulation
If you have a toothache, it's normal to feel more discomfort while sleeping. This is because lying down causes blood to rush to your head and increase pressure on your teeth.Extra blood pressure puts extra strain on a painful tooth, increasing its inflammation. So to reduce pain and swelling associated with this, apply cold compresses or use an ice pack.
(12/20/2024)by Health Buzz
More Information: N
Views: 790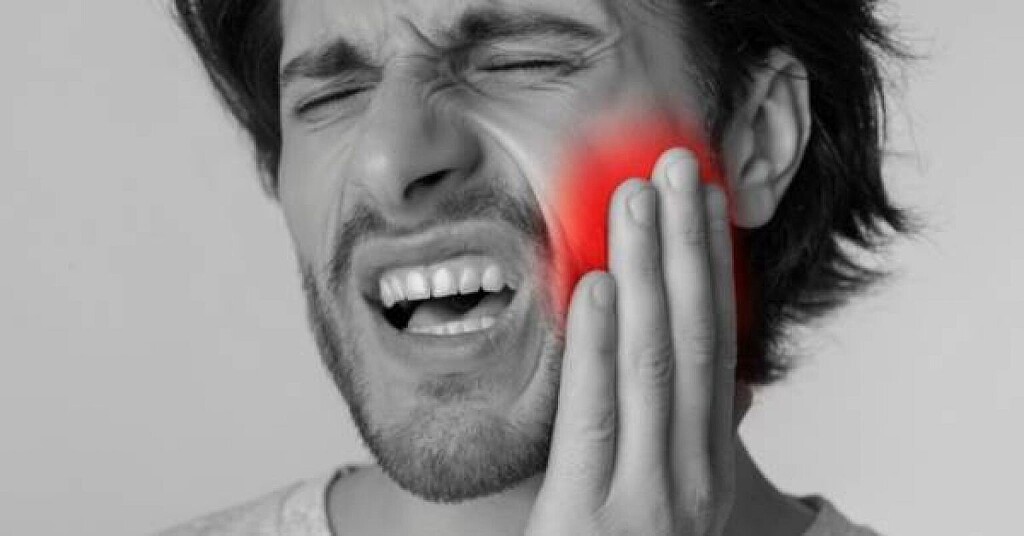
Why Does Wisdom Tooth Pain Come and Go?
Most people know that wisdom teeth pain can be quite severe. But many don’t understand that the pain in wisdom teeth can come and go seemingly for no reason. So why does this happen? And more importantly, what can you do to make the pain go away for good? In this post, we’ll explore those questions and offer some solutions.
Why does wisdom tooth pain come and go?
Your wisdom teeth can cause you a lot of pain. But why does this pain come and go? What could be causing it?
There are several reasons why your wisdom tooth pain might come and go:
1. It is not wisdom tooth pain that you are experiencing
One reason is that the pain might come from another part of your mouth. An infection may cause pain in your gums or a problem with one of your other teeth.
2. Wisdom tooth is growing
Another reason the wisdom tooth pain might come and go is that the tooth itself is still growing.
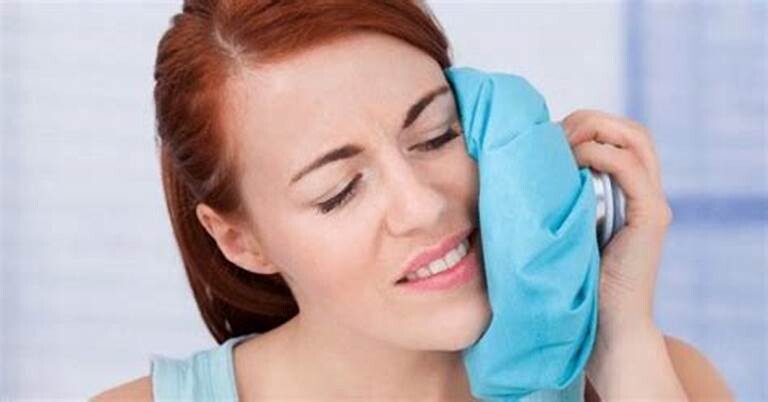

3. Eruption
Finally, the wisdom tooth may be simply erupting. This means the tooth pushes through your gum line and into your mouth. The eruption process can be very painful but usually lasts only a few days. After that, the pain should go away.
If you are experiencing wisdom tooth pain, see a dentist. The dentist will be able to determine what is causing the pain and will be able to provide you with the proper treatment.
What can you do to remove the pain from your wisdom tooth?
If you are experiencing wisdom tooth pain, there are several things that you can do to make the pain go away:
1. Take over-the-counter pain medication
One of the easiest ways to reduce wisdom tooth pain is to take over-the-counter pain medication. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are both effective at reducing pain. Be sure to follow the instructions on the label carefully.
2. Apply a cold compress
Another way to reduce wisdom tooth pain is to apply a cold compress to the affected area. This will help to numb the area and reduce inflammation.
3. Rinse with salt water
Rinsing your mouth with salt water can also help to reduce wisdom tooth pain. The saltwater will help to reduce inflammation and will also kill bacteria that might be causing the pain.
4. See a dentist
If the pain is severe, you might need to see a dentist. The dentist can prescribe more vital medication or can provide other treatments that will help to reduce the pain.
5. Home remedies
Several home remedies can help with wisdom tooth pain:
Clove oil is an effective natural remedy for toothache pain.
Peppermint tea bags have also been found to help relieve wisdom tooth pain.
Another home remedy is to mix one tablespoon of baking soda with two tablespoons of water. This mixture can be used as a mouthwash or applied directly to the affected area with a cotton ball.
If you are experiencing wisdom tooth pain, there are several things that you can do to make the pain go away. Be sure to see a dentist if the pain is severe or if it does not go away after trying these home remedies.
When to see a dentist about wisdom teeth?
If you are experiencing wisdom tooth pain, it is vital to see a dentist. The dentist will be able to determine what is causing the pain and will be able to provide you with the proper treatment. In some cases, the pain might be caused by an infection or a problem with one of your other teeth. If this is the case, the dentist will be able to prescribe antibiotics or other medication to help treat the issue.
The dentist can prescribe more vital medication or can provide other treatments that will help to reduce the pain.
Conclusion
Wisdom tooth pain can come and go for a variety of reasons. In most cases, the pain is caused by the eruption of the wisdom tooth. The tooth can cause pain as it moves into position in your mouth. Other causes of wisdom tooth pain include infection, problems with another tooth, or gum disease.
You can do several things to numb the pain.
Suppose you can see a dentist for proper treatment. You can do several things to reduce the pain, including taking over-the-counter medication, applying a cold compress, rinsing with salt water, and using home remedies like clove oil or peppermint tea bags.
(12/20/2024)by Planitation Smiles
More Information: N
Views: 751
How Long Should I Brush My Teeth?
The importance of brushing for the full two minutes is an oft-repeated piece of advice that dentists give to patients, and parents give to children. But is there science to back this up? Why two minutes and not one or four? How long should you brush your teeth to maintain good oral health? The fact is, brushing your teeth correctly and thoroughly is essential for healthy teeth and gums, but it takes time ― at least two minutes.
What the Experts Say
Experts who advise on how long you should brush your teeth usually recommend a minimum of two minutes, twice daily. A study published in the British Dental Journal examined 66 sources of dental information from around the world and found that a significant portion of them (26) advised brushing for two minutes. The remaining sources offered a number of different recommendations, all longer than two minutes, with some recommending brushing for more than three minutes. The American Dental Association backs the two-minute rule, and runs a campaign called 2min2x to help parents get the message across to children.
What the Science Says

Research supports the recommendation to brush for at least two minutes. It seems obvious that the longer you brush your teeth, the more plaque you remove, and now a study published in The Journal of Dental Hygiene backs this up. The study analyzed the effect of brushing time on plaque removal across a range of time periods, from 30 seconds to three minutes. The researchers found that patients who brushed for 45 seconds removed 26 percent less plaque than patients who brushed for two minutes. The difference in plaque removal when comparing shorter and longer brushing times was even wider: according to the study, brushing for 30 seconds removes 55 percent less plaque than brushing for three minutes.
Why Brushing Your Teeth Takes Two Minutes
Two minutes may feel like an awfully long time when brushing your teeth, but only if you are not doing it thoroughly. Removing food debris, plaque and bacteria from the surface of your teeth is only one step in an effective, twice-daily oral-care routine.

As well as setting up home on your teeth, bacteria also coat your mouth's interior, including the inside of your cheeks, your gums and your tongue. To reduce your risk of bad breath and cavities, you should brush these areas too. Once per day, you'll need to spend just a little longer cleaning your teeth via flossing, because that's also a critical step toward good oral health.
How long should you brush your teeth? As long as it takes to do a good job. For some people, two minutes is long enough, for others, it may take longer. For that clean mouth feeling and the confidence that you are helping prevent tooth decay, the time spent is worth it.
(12/19/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.unitedconcordia.com/business-services/employers/blog/long-brush-teeth
Views: 648
What Are the Signs of Gum Disease?
Gum disease is a serious infection of the gums that, left untreated, can cause irreparable damage to the gums and destroy the bone around affected teeth. According to Australia’s Oral Health Tracker, most Australians are affected by this largely preventable disease at some stage in their life. While you can reverse the first stage of gum disease, you cannot do the same for later stages. Therefore, you should always watch out for early signs and take appropriate action. Take care of your teeth at home through good oral hygiene and make regular visits to your dental proffesional to monitor the health of your gums.
Signs of gum disease at each stage
The early stages of gum disease can go unnoticed with only minor signs and symptoms, while the later stages of disease are far more obvious. Here are the three stages of gum disease and their signs:
• Gingivitis: The first and reversible stage of gum disease, called gingivitis, occurs when plaque buildup allows bacteria to irritate your gums. You might notice bleeding when you brush your teeth, swollen gums or redness, according to the Department of Health Services Victoria. Many people write these symptoms off as a sensitive mouth or the result of brushing too harshly, without realising that they might be on their way to a more serious oral health problem.

• Periodontitis (mild to moderate): The second and irreversible stage of gum disease is called periodontitis and occurs when gingivitis is not treated in susceptible people. Signs may include bleeding, swelling, bad breath, receding gums, and a bad taste in the mouth.
• Advanced periodontitis: The final and irreversible stage of gum disease, called advanced periodontitis, destroys the fibres and bone supporting your teeth to such an extent that your teeth may move, loosen or possibly require removal.
Gum disease prevention at home
When brushing your teeth, always brush your upper and lower teeth gently for at least two minutes. Tilt the brush at a 45° angle against the gum line, and roll or sweep the brush away. Gently brush the inside, outside and chewing surface of each tooth using short back-and-forth strokes (much like a vibration of the brush or small circles). And don’t forget your tongue. By gently brushing your tongue, you can remove bacteria and freshen your breath. Using an antibacterial toothpaste and/or mouthwash can help control plaque formation even further.
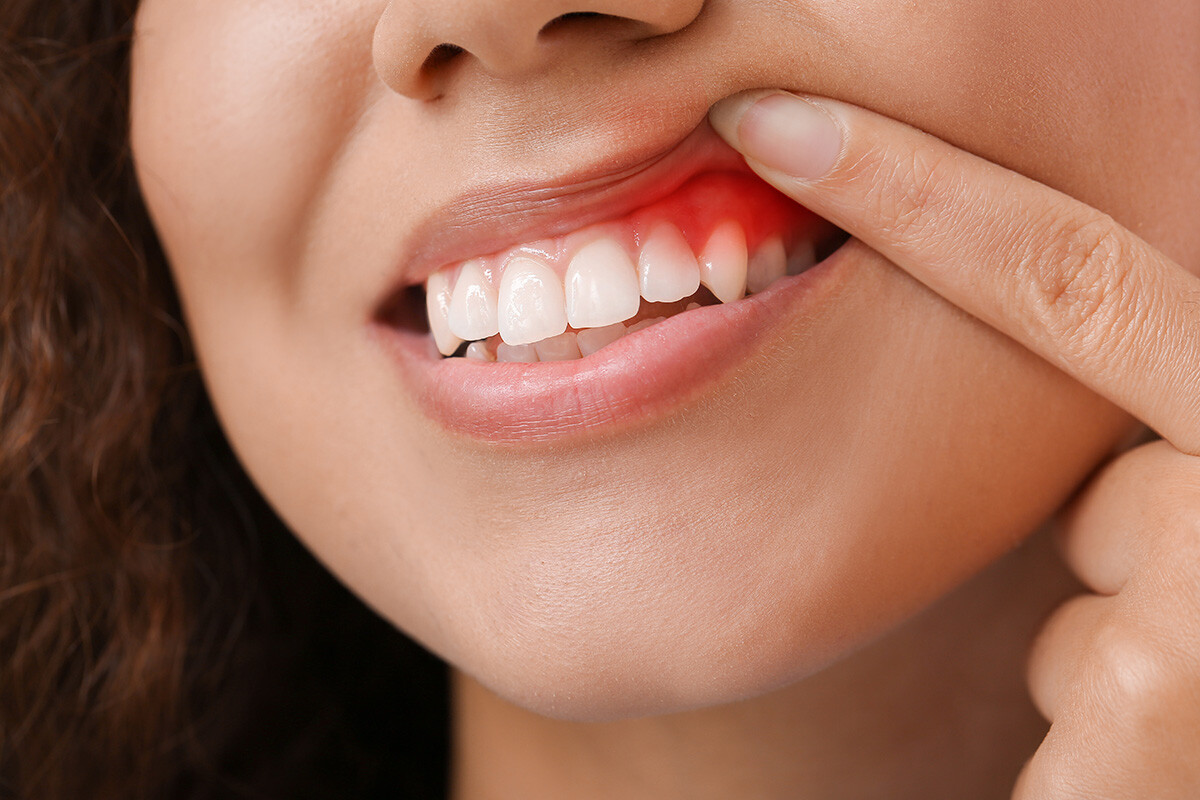

Do the above routine each morning and night. Finally, make sure you floss once a day to remove debris stuck between your teeth. After flossing, rinse your mouth well to get rid of food particles and bacteria.
Regular dental visits
While proper brushing and flossing go a long way towards keeping gum disease at bay, regular dental visits are important for removing plaque and tartar. And by removing plaque, you help prevent gingivitis.
Most dental professionals recommend a routine dental check-up every six to 12 months; however, these recommendations vary. Ask your dental professional how often you should visit, and always stay on the lookout for signs of gum disease. According to the Australian Dental Association, if you notice that your gums bleed when you bite into food or brush/floss your teeth, it’s time to see your dental professional for a periodontal check-up as soon as possible.
(12/19/2024)by United Concordia Dental
More Information: N
Views: 647
Can a Badly Decayed Tooth Be Saved?
Healthy teeth play a crucial role in both our physical and mental health. Furthermore, teeth also influence our appearance, affect our smile, and are essential for eating and speaking without discomfort.
Despite knowing how crucial teeth are for our overall appearance and health, unfortunately, many people fail to address tooth decay until it’s too late. It is essential to consult a dentist if one or more teeth are decaying. The sooner you realize it, the better it is for your oral health.
Often deep tooth decay leads to tooth extraction. However, there are other treatments also available to replace your damaged tooth. So, is it possible to save a badly decayed tooth?
How does tooth decay occur?
Decayed Tooth is damage to your teeth, potentially resulting in cavities, dental abscesses, or tooth loss in some cases. Bacteria present in dental plaque cause tooth decay.
The bacteria in plaque convert the sugars present in your food into acids. These acids will begin to damage your teeth if you allow plaque to build up over time. Therefore, good oral health is pivotal in preventing your teeth from decaying.
Tooth decay occurs in various stages. Let us explore these stages and find out how you can stop tooth decay from spreading.
What are the different stages of tooth decay?
Dental plaque is a colourless, sticky film that covers the surface of your teeth, made up of bacteria, food particles and saliva. Plaque builds up gradually if your teeth are not regularly cleaned.
Tooth decay occurs in five different stages in general.
Stage 1: Initial demineralization (White spots)
The outer layer of your teeth is made of a tissue called enamel, mainly made up of minerals. The enamel loses these minerals when a tooth is exposed to acids produced by bacteria.
You may see a white spot on one of your teeth, indicating the initial stage of tooth decay.
Initial demineralization is reversed by treating the teeth with fluoride. Fluoride strengthens the enamel and makes it more resistant to the acids generated by plaque bacteria.
Stage 2: Enamel decay
Your enamel will break down further if you allow the tooth decay process to continue. The white spots on teeth will soon darken to a brownish colour. It can result in cavities as the enamel is weakened.
Dentists use fillings to treat cavities.
Stage 3: Dentin decay
Dentin is a tissue lying under the enamel. It is softer than enamel; therefore, tooth decay occurs faster on reaching dentin.
You may experience sensitivity when having hot or cold food or drinks once the dentin is affected by tooth decay.
Dentin decay is possible to treat with Fillings in the early stage, or the dentist may suggest placing crowns in more advanced cases.
Before placing the crowns, the decayed area is removed first, and if necessary, some healthy tooth tissue may also be removed to ensure that the crowns fit nicely into your mouth.
Stage 4: Pulp damage
The innermost layer of your teeth contains the nerves and blood vessels that keep the tooth healthy. The layer is known as the pulp.
When the pulp layer is damaged, it may swell, hurting you significantly. You will need a root canal treatment that removes damaged pulp, and the crown will be placed on the affected tooth.
Stage 5: Abscess
Bacteria can invade and cause infection if the tooth decay begins to advance into the pulp. Increased inflammation in the tooth can cause a pocket of pus to form at the bottom of your tooth, known as an abscess.
Tooth decay can cause severe pain that may even radiate into the jaw. If an abscess is formed in your tooth, your dentist will primarily perform a root canal treatment to seal the tooth after removing the infection. In severe cases, the affected tooth may also need to be removed.
Stage 3: Dentin decay
Dentin is a tissue lying under the enamel. It is softer than enamel; therefore, tooth decay occurs faster on reaching dentin.
You may experience sensitivity when having hot or cold food or drinks once the dentin is affected by tooth decay.
Dentin decay is possible to treat with Fillings in the early stage, or the dentist may suggest placing crowns in more advanced cases.
Before placing the crowns, the decayed area is removed first, and if necessary, some healthy tooth tissue may also be removed to ensure that the crowns fit nicely into your mouth.
Stage 4: Pulp damage
The innermost layer of your teeth contains the nerves and blood vessels that keep the tooth healthy. The layer is known as the pulp.
When the pulp layer is damaged, it may swell, hurting you significantly. You will need a root canal treatment that removes damaged pulp, and the crown will be placed on the affected tooth.
Stage 5: Abscess
Bacteria can invade and cause infection if the tooth decay begins to advance into the pulp. Increased inflammation in the tooth can cause a pocket of pus to form at the bottom of your tooth, known as an abscess.
Tooth decay can cause severe pain that may even radiate into the jaw. If an abscess is formed in your tooth, your dentist will primarily perform a root canal treatment to seal the tooth after removing the infection. In severe cases, the affected tooth may also need to be removed.
What you should do
If you experience pain or swelling, immediately visit your dentist and see what they say. If the dentist spots cavity or tooth decay, they will usually recommend you a filling as the best treatment option.
Sometimes tooth decay is unavoidable even after having great at-home oral hygiene; in such cases, dental checkups every six months can help identify and address decay at its initial stages.
(12/18/2024)
by Dr.Quadri.
More Information: https://drquadri.com/decayed-teeth-can-a-badly-decayed-tooth-be-saved/
Views: 657
Did You Know You Can Actually Reverse Cavities By Changing Your Diet?
You probably know – at least to some degree – that the foods you eat can affect the state of your gums and teeth. How often you eat them also plays a role. Have too many servings of sugary treats, for example, and you’re more likely to experience tooth decay. It’s not just sugar, of course. Tooth decay is caused by a lack of minerals, vitamins, and other nutrients that are necessary for healthy teeth and gums.
In short, eat poorly and you’re more likely to have poor teeth. From there, it’s a tiny leap in logic to understand that your teeth and gums are more likely to be healthy if you eat well.
Here’s the thing that’s a bit of a surprise for most, though: changing your diet for the better not only slows down decay – it can actually put a stop to it completely!
When you eat and drink well, you provide your teeth with the nutrition they need to avoid decay and limit tooth-destroying acids that too many “bad” foods create. What can you do specifically?
Monitor Sugar and Carbohydrate Intake
Why are sugars and carbohydrates harmful? Because when they combine with the plaque that’s already on our teeth, it creates acids that eat away at your enamel, resulting in cavities.
Because of this, it’s best to monitor sugar and carbohydrate intake by reading the nutritional contents of labels. Select foods that have low sugar levels whenever possible, and limit the number of carbs and starchy foods in your diet.
If carbs are a must, go for whole grains whenever possible. Eating whole grains will help keep your gums and teeth healthy while also providing you with a higher amount of fiber. These options include whole-grain cereals, bread, and more.

Whole grains or not, when you do eat or drink foods higher in sugar or carbohydrates, try to clean your mouth out within a half-hour or so if possible. Brushing your teeth is the best way to do this, but we know that’s not always an option. Alternatives include swigging some mouthwash, chewing sugarless gum, and…
Drink Lots of Water
While water doesn’t have specific nutritional value, it is absolutely the best thing you can drink to help prevent tooth decay and cavities. Why? Because unlike just about every other kind of drink, it does no harm.
That may sound like faint praise, but it really does matter. Water provides you with a way to wash out leftover food and harmful films that may be covering your teeth – including the always-dangerous acids – and it does this without leaving anything bad behind. No other drink can really say this.
Eat a Well-balanced Diet
It’s not enough just to minimize the harmful things you eat. You also need to eat larger amounts of nutritious foods – and more variety. Specifically, you should eat a varied mix from the five food groups: whole grains; fruits; vegetables; lean meats such as beef, fish, or chicken; and dairy products that are fat-free or low-fat.
Bring on the Calcium
Calcium in dairy foods is a great way to help prevent cavities. It also encourages the production of saliva.
Healthy, calcium-rich dairy options include cheese, milk, and yogurt. Beyond dairy products, there are other foods that contain calcium such as greens like broccoli, collard greens, spinach, and lentils, as well as salmon, kale, nuts, and beans.
Opt for High-Fiber
Consuming high-fiber foods will help keep the saliva flowing which aids in the prevention of cavities and tooth decay. This includes dates, figs, and raisins, apples, bananas, and oranges. Other high-fiber foods include peas, Brussel sprouts, and nuts.
Add Vitamins and Supplements to Your Diet
The sad truth is that most of us don’t get the recommended daily amounts of vitamins and minerals from our diets. Working to change what you eat will help this, but even then it’s not easy. Just try getting enough potassium without eating a dozen bananas a day!
Because of this, adding vitamin supplements to your routine can prove beneficial. Vitamins stimulate saliva production, which will help make your teeth much stronger.
Of course, altering your diet only goes so far. You still need to book time with your dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups. The difference is that – if all goes well – they’ll have a lot less work to do!
(12/18/2024)by South Florida Dental Care
More Information: N
Views: 682
A Few Facts to Know About Gum Disease Treatment
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection that damages soft tissue in the mouth and the bone which supports a patient’s teeth. Oral bleeding is normal after certain procedures and if your toothbrush is too hard on your gums; but if you notice chronic bleeding when brushing or if there’s any unexplained bleeding, it could signify gum disease. Thankfully, Wetaskiwin dentists can treat your gums and prevent the disease from spreading.
Gingivitis is the first stage of this condition, and it is characterized by inflammation. This phase of infection is very common and usually goes unnoticed. If you experience tender or swollen gums or bleeding after brushing, it could be an indication that you’ve developed gingivitis. With a good oral hygiene routine, symptoms can go away.
The advanced stage of gum disease is known as periodontitis. This will cause a patient’s gum to detach from their teeth, creating a space or a“pocket” that harbours bacteria and infection, which affects the surrounding teeth, tissues, and ligaments. If left untreated, periodontitis can eventually lead to tooth decay. The infection can also spread to the bloodstream and affect a patient’s general health. Having a dental clinic that offers gum disease treatment in Wetaskiwin is important to ensure your oral health is restored. Wetaskiwin Family Dental is here to help you treat and prevent further infections.
What You Should Know About Gum Disease Treatment
Gum disease can become a dangerous condition if it goes unaddressed. Fortunately, dentists in Wetaskiwin use up-to-date technology and treatments to treat gum disease, including:
1. scaling and planning
This is the first treatment dentists can perform to treat gum disease. Scaling removes the tartar that has accumulated on the tooth and gum line. Your dentist will then reattach your gum to the teeth.
2. Medication
Your dentist may prescribe you antibiotics to help reduce bacteria and help control the infection. The dentist may also recommend other ways to prevent the infection from growing until it can be treated properly with an advanced procedure.
3. Flap surgery
This surgery will eliminate the gum pockets created by the disease. A dentist will make an incision on the gums and reposition them back toward the bone. Once this is done, the bone may need to be contoured (or manipulated) so the gum tissue can attach and heal.
4. Bone graft
If your gum disease has advanced, it can affect your bones. Patients might need a bone graft to rebuild the bone structure affected by the infection.
5. Soft tissue graft
Gum disease can affect your mouth’s soft tissue and cause tissue loss. The dentist will need to get material from the roof of your mouth (also called your palate) and reattach it to the areas that have lost tissue to reinforce and prevent further loss. This will help reduce gum recession.
5. Tooth extraction
When an infection is too developed, the dentist may need to remove the tooth to restore oral health. The tooth can then be replaced with a restoration treatment.
Gum Disease Can Be Prevented
Maintaining a good hygiene routine and visiting a dentist near you for regular check-ups is the best way to prevent gum disease. Make sure you brush your teeth twice daily and floss at least once to prevent plaque accumulation. To remove any additional bacteria, finish your routine with mouthwash. A good hygiene routine at home is not enough, so ensure you schedule cleaning appointments twice a year. During the appointment, a dentist will check for any infection.
If you fear you have gum disease and are looking for gum disease treatment near you, contact Wetaskiwin Family Dental to book an appointment today.
(12/17/2024)
by Wetaskiwin Family Dental
More Information: https://www.wetaskiwinfamilydental.com/a-few-facts-to-know-about-gum-disease-treatment/
Views: 677
What Is Involved in the Process of Deep Cleaning of Teeth?
Did you know that 26% of adults in America have untreated dental decay? Annual deep cleaning of teeth is the key to preventing this type of teeth and gum disease. Unfortunately, many people are scared of going to the dentist. Just the words ‘deep cleaning’ is enough to send some patients off shivering.
Luckily, deep cleaning doesn’t need to be frightening. In this article, we’ll walk you through everything the procedure entails. That way you’ll know exactly what to expect next time you schedule a visit. Let’s get started!
What Is Deep Cleaning of Teeth?
Deep cleaning is different from a regular dental cleaning. This type of procedure goes below the gum line. It does this to clean hard-to-reach spots like the roots and pockets at the base of your tooth. A substance known as tartar can build-up around the exterior and roots of teeth. If left unchecked, then this tartar can cause serious bacterial infections.
As such, dentists use a technique known as periodontal scaling and root planing to remove this substance. If the tartar can’t be removed using manual scraping, then they’ll also use an ultrasonic removal device. This is the main distinction between deep cleaning and regular cleaning. The process of removing tartar can sometimes be quite demanding.
As such, it can last hours and might need to be broken up into multiple sessions. Ultimately, it depends on how bad the case is and how sensitive your teeth are. While a deep cleaning might sound tedious, it’s a vital part of fighting against dangerous infections. If left untreated it can warp into an even worse condition, like a root canal. So how do you know when a deep cleaning is needed?
When is Deep Cleaning Necessary?
The ADA recommends scheduling dentist appointments for intervals recommended by the dentist. There’s no one set answer for how often you should get a deep cleaning. That’s because every unique case requires a different approach. During these visits, your dentist will recommend whether or not you should get a deep cleaning.
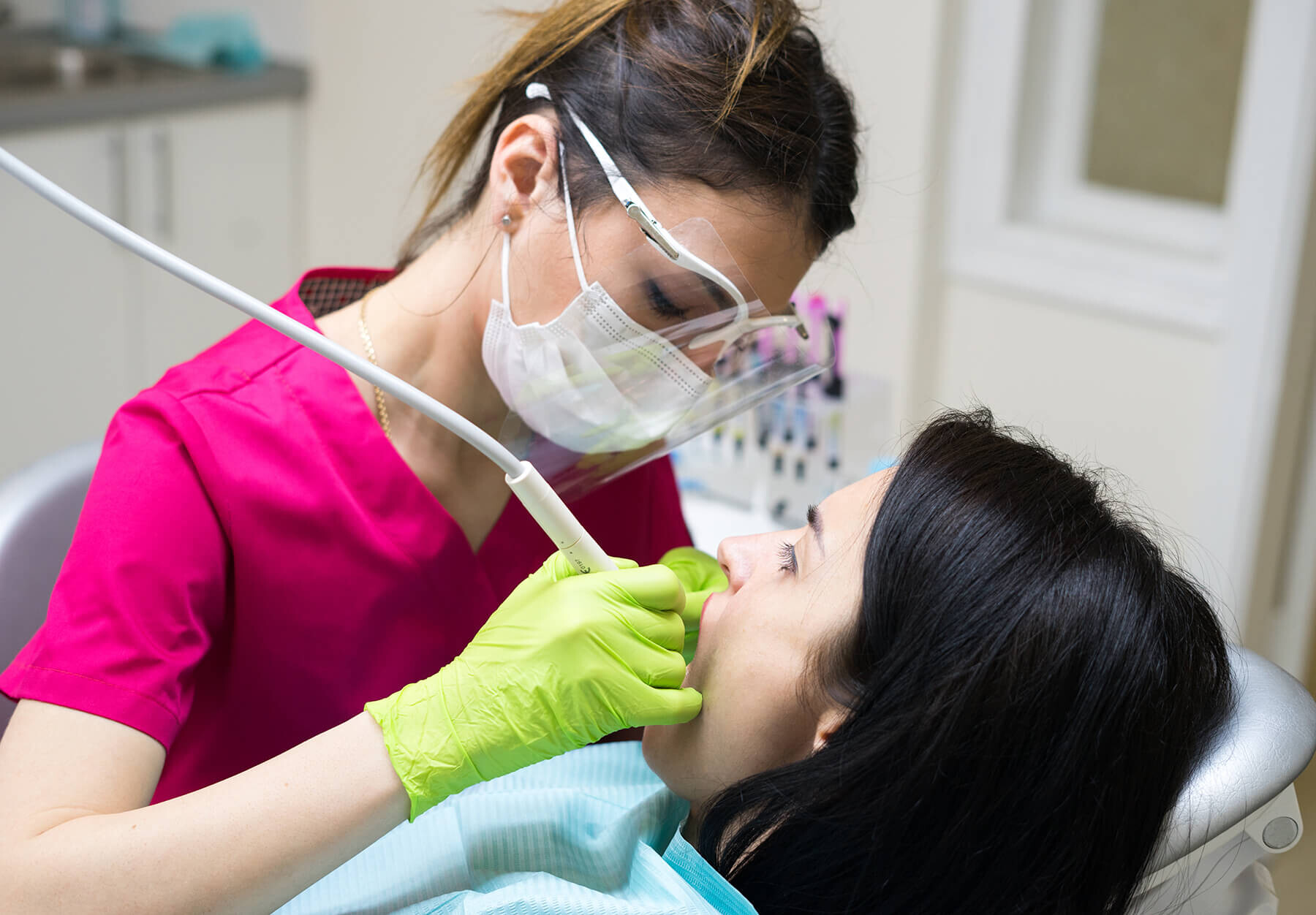

One clear sign of needing deep cleaning is checking for gum disease. You can do this by measuring how far your gums pull away from your teeth. Any pocket that’s more than five millimeters deep will require immediate deep cleaning. Other symptoms of gum disease include things like:
Swelling gums
Bleeding gums
Bruising around the gums
Pus in the gums
Bad smelling breath
Gum disease occurs when bacteria get into pockets and roots of the teeth. Certain types of gum diseases will also require additional treatments. It’s also recommended to get a deep cleaning if it's been more than six months since your appointment with your dental hygienist.
How Does the Procedure Work?
Before the procedure, your dentist will go over your medical history and perform an x-ray. That way, they have a good idea of which areas to focus on. After this preliminary planning stage, the dentist will measure the depths of the gum sockets using a special tool.
This process is also used for probing to determine if the person has gingivitis or periodontitis. After this, the dentist will begin the scaling process. As we mentioned earlier, this is a scraping that removes tartar from the teeth. If needed, an ultrasonic tool is also used. After this, the teeth are polished using a gritty toothpaste.
Then, an air polisher is applied to smooth out the teeth. The dentists may go through final flossing as well. Finally, a fluoride treatment might be used. This process helps remineralize the enamel on your teeth.
Does the Procedure Hurt?
Most of the time, any discomfort associated with the procedure is bearable. However, individuals with particularly deep pockets will be in a lot more pain than others. Similarly, people with sensitive teeth might be incredibly uncomfortable. As such, a dentist will administer a local anesthetic as it’s needed. This will just numb the area around your gum.
How Much Does the Procedure Cost?
The cost of deep teeth cleaning can vary depending on the severity of the case. More gum disease and inflammation will require more work to fully clean. As such, it will be more expensive. You’ll likely have two separate visits, or more if the damage is extensive.
Typically, dentists charge for each quadrant of the mouth that’s deep cleaned. The average cost is usually $100 per quadrant. But this can change depending on where you live. If you have dental insurance, then you should check your plan. Many insurance providers cover deep cleanings.
What to Expect After Deep Cleaning
Typically after the cleaning, you'll experience slight soreness of the gums. As such, you should avoid hot, crunchy, hard, acidic, and sticky foods. We also recommend brushing with toothpaste for sensitive teeth.
You might notice some bleeding when you first start brushing, but this shouldn't last long. If you can help it, try to avoid brushing the affected area. Also, you should wait one week to floss so you don't agitate the gums. If you notice swelling, then try washing with a saltwater solution.
Ready to Schedule Your Deep Cleaning? Contact Sparkle Dental
We hope this article helped you learn more about what happens when you schedule a deep cleaning of teeth. As you can see, there is little to worry about when it comes to this type of procedure. All you need is a dental practitioner that you can trust. So how do you find one? If you live in Mt. Vernon, Yonkers, or New Rochelle area of New York, then look no further than Sparkle Dental.
(12/17/2024)by Sparkle Dental
More Information: N
Views: 709
Glossitis: What to Know About Inflammation of the Tongue
The tongue is a small, muscular organ in the mouth that helps with tasting and swallowing food, as well as articulating speech. On occasion, however, the tongue may develop glossitis, a condition that causes it to swell, become red in color, and develop a smooth appearance on its surface.
There are a variety of different things that can cause glossitis and different types that a person can develop—both of which we’ll be discussing today, along with symptoms to look out for and how it is diagnosed and treated. Read on to find out more about glossitis with these 12 facts.
1. Type: Acute Glossitis
There are several different types of glossitis, one of which is referred to as acute glossitis. According to Healthline, this type causes “inflammation of the tongue that appears suddenly and often has severe symptoms.”
In addition to swelling, other severe symptoms include pain and shortness of breath (known medically as dyspnea). Acute glossitis most commonly occurs due to an allergic reaction or from trauma to the tongue, such as burns or bites.
2. Type: Chronic Glossitis
With chronic glossitis, inflammation of the tongue occurs on a long-term basis, and “may begin as a symptom of another health condition,” says AARP.org. Interestingly, chronic glossitis is more common than acute glossitis.
One subtype of chronic glossitis is known as chronic superficial glossitis, because it’s not the tongue itself that becomes inflamed but rather the mucous membrane that covers it. This particular type is especially common among alcoholics, tobacco users, and those who have chronic stomach or intestinal diseases.
3. Type: Atrophic Glossitis
According to Prime Health Channel, atrophic glossitis (also known as Hunter glossitis) “derives its name from the fact that the tongue gets washed away of its original color to assume a beefy red color and is automatically smoothened.”
And by smoothened, the source means that the tongue loses many of its papillae, which are the small bumps that normally cover the surface of the tongue. This can give the tongue a “glossy appearance,” says Healthline.
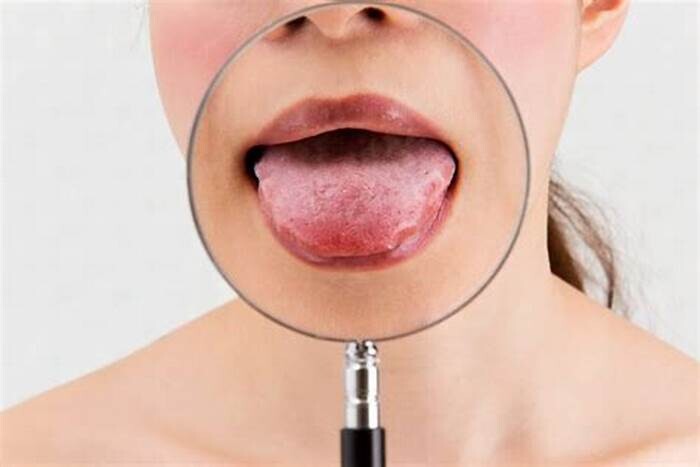
4. Type: Idiopathic Glossitis
Idiopathic glossitis “…is characterized by the inflammation of the mucous membrane and the overall muscle of the tongue,” says Prime Health Channel. Unfortunately, however, the cause of this particular type of glossitis is unknown.
As with atrophic glossitis, those with idiopathic glossitis will develop a smoothened tongue, often losing “up to 50-percent or more of the papillae,” says AARP.org, giving it the same glossy appearance.
5. Cause: Allergic Reactions
One of the most common causes of glossitis—particularly acute glossitis—is an allergic reaction. These allergic reactions may be to “medications, food, and other potential irritants that may aggravate the papillae and the muscle tissues of the tongue,” says Healthline.
Certain medications used to treat high blood pressure—known as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors—are particularly common irritants, as are “mouthwash, breath fresheners, toothpastes, plastic in dentures, [and] dyes in candy…” indicates Prime Health Network.
6. Cause: Disease and Infections
Glossitis may also occur as a result of contracting a disease, particularly those that affect the body’s immune system, as they may “attack the tongue’s muscles and papillae,” says Healthline. Herpes simplex, “a virus that causes cold sores and blisters around the mouth,” is one such example.
Infections can also cause glossitis, including those caused by bacteria, yeast, or fungi (such as thrush, which produces “white patches on the tongue and inside of the mouth,” says WebMD). Poor oral hygiene and low saliva production (dry mouth) can also lead to infections, which increases a person’s chances of developing glossitis.
7. Cause: Vitamin Deficiencies
Another common cause of glossitis is vitamin deficiency. If you’re not getting enough iron, for instance, low myoglobin levels may result. This can lead to glossitis because “myoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that’s important for muscle health, including the tongue’s muscle tissue,” says Healthline.
Other vitamin deficiencies that can cause glossitis are vitamin B12, vitamin E, riboflavin, folate, and niacin. Regardless of which vitamin is the culprit, this type of glossitis is aptly referred to as glossitis vitamin deficiency.
8. Cause: Mouth Trauma or Injury
As mentioned earlier, trauma or injury in the mouth can lead to glossitis as well. Common examples include biting, cutting, chewing, or burning tissue of the tongue or elsewhere in the mouth. Additionally, inflammation may be caused dental appliances, such as braces or ill-fitting dentures.
And while it may look cool, piercing the tongue also increases the likelihood of developing glossitis, as it makes the muscular organ more susceptible to infections and wounds.
9. Symptoms
Although we’ve already mentioned several of the symptoms of glossitis, they are worth repeating. Pain or tenderness in the tongue is among the most common to be mindful of, as is swelling or inflammation.
In some cases, this swelling may become so severe that it affects a person’s ability to swallow, chew, or speak. If this occurs, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. The tongue may also change color, becoming pale or bright red, and take on a smooth appearance due to loss of papillae.
10. Diagnosis
When it comes to diagnosis, the U.S. National Library of Medicine says that your dentist or doctor will assess your condition by doing an exam to look for “finger-like bumps on the surface of the tongue (called papillae) that may be missing” and a “swollen tongue (or patches of swelling).”
Additionally, the individual conducting the exam may ask questions about your medical history and lifestyle in an effort to determine the cause of glossitis. Samples of blood and saliva may also be taken to help confirm the diagnosis.
11. Treatment: Medications
How glossitis is treated largely depends on what is causing the condition to occur. “If glossitis stems from a bacterial, fungal or yeast infection,” the Colgate-Palmolive Company says, “your medical or dental professional may prescribe a medication to alleviate the symptoms and heal the infection.”
In combination with antibiotics or other medications, topical corticosteroids may also be prescribed and are intended to help reduce symptoms of pain and redness in the tongue or other areas of the mouth.
12. Treatment: Home Care
In other cases of glossitis, home care procedures may be the best course of treatment. If the condition is caused by a virus, for instance, the Colgate-Palmolive Company says “…a doctor can recommend a routine plan to treat the symptoms at home. This plan involves keeping your tongue and whole mouth healthy by brushing twice daily and flossing.”
Or, if the glossitis is caused by a deficiency in certain vitamins, Prime Health Channel indicates it may be best treated by “preparing a diet chart and that is rich in the deficient nutrients.” And in cases where glossitis is due to an allergic reaction or irritant, it is important to identify the cause and eliminate or avoid it to prevent future reactions.
(12/16/2024)by Active Beat
More Information: https://activebeat.com/your-health/glossitis-12-things-to-know-about-inflammation-of-the-tongue/
Views: 783
Foods That Prevent Tooth Decay And Cavities Naturally
How to Prevent Cavities and Tooth Decay
It's no fun passing up sugary treats like cookies and candies. But when it comes to tooth decay, food choices play an important role. Some foods can harm your teeth, while others contain essential nutrients to keep them healthy and strong. To help prevent tooth decay, keep the following food choices in mind.
Calcium
Calcium is a prime ingredient for preventing tooth decay, especially for growing children. Dairy is a great source, with choices such as milk, yogurt and cheese. And calcium isn't hiding in the fat, so skim milk and low-fat yogurt are just as good. Other options are leafy greens such as broccoli and bok choy, canned fish with bones, almonds, Brazil nuts and dried beans.

Fruit, Fiber and Veggies
Eating high-fiber foods keeps saliva flowing, which helps create mineral defenses against tooth decay. Good sources of fiber are dried fruits such as dates, raisins and figs, and fresh fruits, like bananas, apples and oranges. Other options include veggies, such as beans, Brussels sprouts and peas, along with peanuts, almonds and bran.
Whole Grains
Whole grains provide B vitamins and iron, which help keep gums healthy. Whole grains also have magnesium-an important ingredient for bones and teeth. In addition, whole grains are high in fiber. Look for foods such as bran, brown rice, and whole-grain cereals and pasta to be good sources of whole grains.

Avoid Foods that Cause Cavities
When looking to follow a healthy diet that's good for your teeth and the rest of your body, try sticking to the food pyramid. The pyramid is structured to give you a healthy serving of all the necessary food groups you need throughout the day.
Sugar Snacks
When you get the munchies, focus on choosing healthy foods, like the ones we mentioned earlier. Try to steer clear of sweets, because sugar partners with plaque to weaken enamel, leaving you vulnerable to tooth decay. In fact, each time you eat a sugary snack, your teeth are under siege for the next 20 minutes. Brushing with an Oral-B electric toothbrush after eating sugary snacks can help prevent plaque buildup and the onset of tooth decay.
(12/16/2024)
by Oral B
More Information: https://www.oralb.co.uk/en-gb/oral-health/conditions/cavities-tooth-decay/foods-that-prevent-tooth-decay-cavities-naturally
Views: 599
Fissured Tongue: Causes and Treatment
Fissured tongue causes a change in appearance of the tongue. Discover the causes of the disorder and what you can do if you have it.
A fissured tongue is a benign abnormality that occurs on the tongue surface. Although it may appear unsightly at first glance, it doesn’t really affect people’s lives.
The normal tongue is flat along most of its length. A fissured tongue has a deep groove in the middle and may also have small fissures on the surface. This gives it a wrinkled appearance.
This condition isn’t serious in itself, is usually painless, and isn’t contagious. According to the American Academy of Oral Medicine, fissured tongue occurs in 5% of the U.S. population. It tends to occur more frequently in young males.

As we’ll tell you today, its origin is usually associated with hereditary causes and the symptoms become more evident as a person ages. However, in some cases, it can be associated with certain diseases, so it’s advisable to seek an accurate diagnosis.
In this article, we’ll tell you the characteristics of fissured tongue, its causes, and how it’s treated. Read on and learn all about this oral condition.
What is fissured tongue?
Fissured tongue is a benign condition that affects the normal anatomy of the lingual organ. It’s also called scrotal tongue, because of its similarity to the appearance of the scrotum.

As the name implies, the surface of the tongue has multiple fissures or cracks. These may appear on the dorsum of the tongue or extend to the sides.
In general, there’s usually a median fissure in the center of the tongue and several cracks on the rest of the surface. The size and depth of these cracks vary from case to case, but usually range from 2 to 6 millimeters (up to 0.23 inches). The grooves may be connected to each other, making the tongue appear to be composed of separate lobes.
This condition usually doesn’t cause pain or discomfort. However, some people who have it often have tongue swelling, bad breath, and increased sensitivity to certain substances and flavors.
Signs of fissured tongue can occur as early as childhood; however, they become more evident and noticeable as the person ages.
Men are slightly more likely to suffer from fissured tongue than women. Older adults who, in turn, have dry mouths tend to have more obvious symptoms.
It’s important not to confuse this anomaly with migratory glossitis, or geographic tongue. This disorder is characterized by depapillated areas on the tongue surface. These are seen as rounded red spots with whitish edges, which change place over time. Although it’s important to differentiate between these disorders, there are cases of people with both abnormalities on their tongue.
Symptoms of fissured tongue
The main characteristic of fissured tongue is the wrinkled appearance of the lingual organ. A crack in the center of the tongue and several irregular grooves on the rest of its surface alter the flat appearance.
Cracks are usually asymptomatic, that is, they don’t cause pain or discomfort to the patient. However, there are occasions in which some of the following occur:
Pain
Bad breath or halitosis
Swelling or inflammation of the tongue
Discomfort or burning to certain stimuli and substances
If there is no proper oral hygiene, candidiasis may develop.
Complications
Beyond the possibility that some of the symptoms we have told you about may appear, patients with a fissured tongue may experience discomfort. The most common complication is the development of an infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans (oral candidiasis).
This infection can arise as a result of various situations, however, the most common is inadequate oral hygiene. The accumulation of bacteria inside the tongue fissures affects the balance of the normal flora of the mouth and favors the proliferation of fungi.
Candidiasis on the tongue causes white or red lesions, pain, burning, and inflammation. If not treated in a timely manner, it affects the normal functions of the mouth, such as eating, swallowing, and speaking.
To prevent the occurrence and aggravation of this fungal infection, it’s essential for patients with cracks on their tongues to maintain thorough oral hygiene. Special attention to cleaning the tongue is key.
This removes food debris and bacteria that accumulate in the fissures, and prevents infection. In addition, removing tongue debris also prevents the development of bad breath.
Common causes of fissured tongue
A precise cause of cracked or fissured tongue hasn’t yet been identified. On the one hand, it could be due to genetic or hereditary factors, or it could be associated with a different underlying condition.
Fissured tongue can be congenital and appear from birth or develop throughout a person’s life. As we have already told you, the symptoms tend to increase with age.
The hereditary and genetic factors are among the most relevant in explaining the onset of the disorder. Often, several members of the same family have these particular languages.
In addition, this condition is often a symptom of other conditions, such as Down syndrome or Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome. In sone cases, the occurrence of this condition is associated with other health conditions:
Psoriasis
Diabetes mellitus
Vitamin B deficiency
Bruxism, stress and anxiety
Allergic reactions to some foods or medications
Using alcohol and tobacco: these substances cause dry mouth, which favors the appearance of cracks in the tongue.
Treatments for fissured tongue
Fissured tongue doesn’t require any specific treatment to reverse it. However, certain hygiene practices will be necessary to help keep this organ healthy and functional and prevent associated complications.
To do so, it’s important to visit the dentist frequently. In order to obtain an accurate diagnosis, it’s necessary to rule out other lesions and understand how to take care of fissured tongue.
Regular dental check-ups every six months allow the dentist to evaluate the state of the tongue and rule out the presence of other pathologies. If mycosis or other infections develop, the dentist can initiate the appropriate treatment.
It’s also a good idea to visit the dentist if the tongue starts to burn, itch, or hurt. These symptoms may be indicative of a complication.
On the other hand, in addition to check ups, there are some simple practices that can prevent complications associated with a fissured tongue. We’ll tell you about them.
Strict oral hygiene
Keeping the oral cavity clean is one of the best strategies to prevent fissured tongue complications. Food debris and bacteria can accumulate in the crevices of the tongue, causing bad breath, and promoting infections.
It’s important to brush with fluoride toothpaste and floss to remove plaque from the mouth. In addition, special attention should be paid to cleaning the tongue.
To do so, it’s best to use a tongue scraper, or tongue cleaner. This is an instrument that’s specially designed to thoroughly clean the irregular surface of the tongue.
Cleaning consists of moving the instrument back and forth several times over the entire tongue surface. This allows you to get rid of debris and bacteria trapped in its grooves or cracks.
Not having a tongue scraper is no reason not to keep your tongue healthy. Keeping a toothbrush for this purpose, or using the back of the toothbrush head are two options.
Tongue hygiene should be carried out at least once a day. However, in patients with fissured tongue, increasing the frequency may be of greater benefit.
Supplementing cleaning with oral rinses is a way to remove debris that can’t be reached with a scraper. At the same time, you will obtain fresh, clean breath.
Reduce the consumption of irritating foods
A burning or itching sensation on the tongue on contact with certain substances is another complication that can appear in people with tongue fissures or cracks. Avoiding highly acidic, salty, bitter, and spicy foods is one strategy to prevent irritation.
Proper and frequent tongue brushing, proper nutrition, and the absence of harmful habits help prevent infection and discomfort. Twice-yearly visits to the dentist complete the care routine, in order to ensure that fissured tongue doesn’t become a problem for the sufferer.
(12/14/2024)by Step To Health
More Information: N
Views: 682
What To Look For When Choosing The Right Dentist For You
“I have an excellent doctor! You should go see her… cos she’s just lovely!”
Phrases like this make me cringe. How is it that so many people measure professional expertise with personality? Imagine picking the best brain surgeon to operate on your wife based on their great sense of humour!
Years ago, my husband went to a doctor. The doctor asked him a few questions and quickly summarised with “so what would you like today?”. So he simply listed his wishes – a new prescription for my cholesterol medicine, a referral to a sleep study because my wife thinks I might have sleep apnoea, and a medical certificate for today please! I listened in horror as my husband reported back later that the doctor promptly wrote all 3 requested documents and completed the consultation very satisfied that he had another happy customer. No, there was no discussion about the fact he was pre-diabetic and had gained significant weight over the past year. He didn’t even check what his last cholesterol results were. Although my husband was quite happy with himself for yet another task ticked off efficiently, I was less than impressed.
Choosing the right family dentist is a lot like choosing the right doctor for your family. Sure, there are times when all you need is a flu shot, medical certificate or a prescription. It’s tempting just to opt to see anyone who can provide that one thing you want at the drop of a hat – someone who can get you in quick and let you get on with your life as quickly as possible.
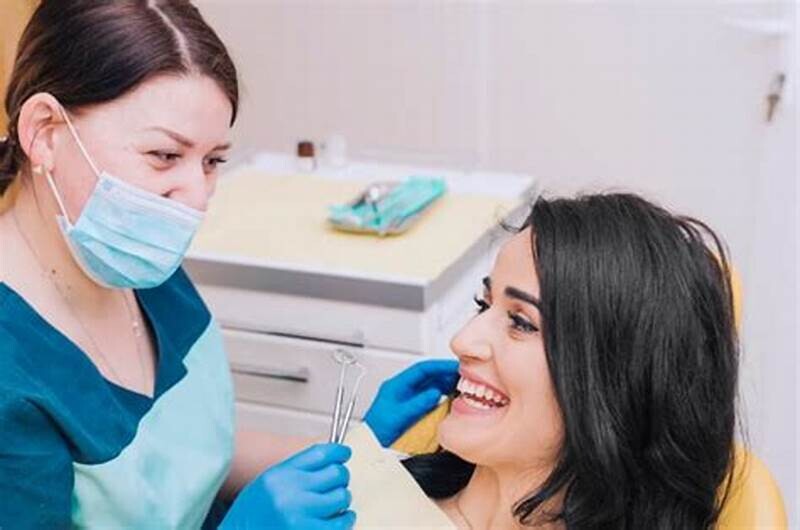

The dental professional equivalent of this is having a go-to dentist who only patches up the odd broken tooth or lost filling. Someone to serve the purpose – clean your teeth, or extract the badly infected tooth and send you away with no expectation to meet again until the next bad thing happens.
I firmly believe that the dentist-patient should begin with a good rapport, but that is only part of the whole package. To help you find the right dentist for you and your family, below are a few aspects to consider.
1. Someone who is in tune with preventing future problems is there with you in the long haul.
A dentist who is committed to long-term patient care is not that hard to pick. They will first listen to your initial concerns and offer solutions to fix the problem. However, she will also offer you valuable insight into why this happened, what other issues could be linked to your initial complaints. Most importantly, she will let you know where you are headed in terms of your future condition.
Let’s use an example: You tell the dentist that you broke a tooth. She can quickly offer to patch this up with a filling or secure it with a crown. Seems quick and simple.
But what if this dentist also took the time to ask you if you have a tendency to grind or clench? Perhaps she touches your neck and facial muscles to see if they have been overworked from the clenching? Do you wake up with headaches or neck pains often? Have you had many teeth or a filling break in a similar way? Next comes the discussion of today’s repair (of course, that’s what you wanted right?) along with the possibility that there could be an underlying cause that could mean anticipating and planning for similar issues with broken teeth in the near future.
The truly amazing doctors are inquisitive and perceptive – that is, they make observations and check the little things that you never realised were relevant to the big picture.
2. Someone who gives you all options but supports your decisions 100%.
As a child, I observed my parents accepting exactly what their doctors and dentists told them they must do. It was the doctors who made decisions about the patient’s treatment. So much so that even now, there is still a whole generation of patients who turn up 6 monthly and literally say, “Don’t tell me anything. Just do whatever you want, I’m in your hands”.
Things are different now thanks to the principle of “informed consent”. As the patient, you have to take responsibility for your own health, so it only makes sense if you also take on the responsibility of choosing the strategies to manage your health issues. But you can only do that if you have the information to help you make the choice that is right for you.
A clinician worthy of your trust is someone who helps you to understand the problems you are facing and gives you strategies to solve them in a way that you can live with.
For example, you may be missing some teeth and wish to get these replaced. The dentist tells you that you can choose a denture, a bridge or an implant and gives you the associated costs. You’d love to have an implant but it is too expensive for right now. Here’s where you could be going home feeling awful that you can’t afford the best and will have to live with a gap for years to come. If you find a dentist who reassures you, “That’s alright. If a denture is a thing you can budget for right now, I will help you get the best denture possible. And we will support you as best we can, keeping the other teeth healthy.” If you feel pressured that you will only be cared for if you choose the most complex solution, then keep looking. You deserve to find someone who not only gives you the information you need but wholeheartedly supports you to make the decisions that are right for you – even if it’s not the most expensive option on offer.
3. Someone who is at the forefront of the latest research and techniques.
Research and development of technology have evolved so rapidly in the last few decades. It’s a really exciting time to be alive!
A dentist should be equally excited to be practising their craft in this age. Even if you have had minimal issues with your oral condition in the past and you always get a good report after your clean and dental check-up, don’t be afraid to ask your dentist, “What’s new?”.
Someone actively keeping up with the latest findings and technology can hardly contain their joy at the possibility of new ways to help their patients achieve a stronger and healthier future. Now not all these developments are necessarily new things you personally will need, but it’s good to know that your dentist is equipped with the latest information. It’s also handy to keep in mind that a good clinician also has enough humility and confidence to acknowledge when there is a need to call on colleagues with a different set of special skills or fields of interest to best help their patients.
The relationship between doctor and patient is very personal and based on trust. I hope everyone can find a dentist who truly cares about and supports their long-term health. When you do, ask them if they would also care for your family and friends too.
(12/14/2024)by Myers Street Dental Clinic
More Information: N
Views: 559
Can An Infected Tooth Cause Cold And Flu-Like Symptoms?
Did you know that a bad tooth can cause more than just dental pain? It turns out that an infected or decaying tooth may actually be linked to cold and flu-like symptoms. While it may seem strange, the connection between oral health and overall well-being is becoming more apparent.
In this article, we will explore how a bad tooth can potentially contribute to cold and flu symptoms and what you can do to prevent this from happening. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of dental health and its impact on our immune system.
Connection between Bad Teeth and Cold and Flu Symptoms
Yes, you read that right – a bad tooth can actually cause cold and flu-like symptoms. Let's explore the connection between bad teeth and cold and flu symptoms in more detail.
First and foremost, it's important to understand what we mean by a "bad tooth." A bad tooth refers to a tooth that is significantly decayed, infected, or damaged. This can occur due to poor oral hygiene, a high sugar diet, trauma to the tooth, or other dental issues.

So how exactly can a bad tooth cause cold and flu-like symptoms? The key lies in the proximity of the tooth to various structures in your mouth and head. When a tooth becomes infected or decayed, it can lead to the formation of an abscess – a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection.
This abscess can result in the spread of bacteria throughout the body, leading to systemic symptoms similar to those experienced during a cold or flu. Here are some common cold and flu-like symptoms that can be caused by a bad tooth:
Fever: An abscessed tooth can cause your body temperature to rise, resulting in a fever. If you're experiencing a fever along with other flu-like symptoms, it's worth considering a dental check-up.
Fatigue: Dental infections can put a strain on your immune system, causing you to feel tired and run down. If you're feeling unusually fatigued, it could be due to a dental issue.
Sinus congestion: The roots of your upper teeth are located close to your sinuses. If a tooth infection spreads to the sinuses, it can cause congestion, stuffiness, and a feeling of pressure in your face.

Facial pain: Infected or decayed teeth can cause facial pain, which can often be mistaken for sinus pain. If you're experiencing facial pain along with other cold or flu-like symptoms, it's important to rule out dental issues.
Swollen lymph nodes: Infections in the mouth can cause the lymph nodes in your neck and jaw to become swollen and tender. If you notice swollen or painful lymph nodes, it may be a sign of a dental problem.
If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, it's crucial to seek dental care as soon as possible. Your dentist will be able to assess the condition of your teeth and determine if a bad tooth is the cause of your cold and flu-like symptoms.
Luckily, treating a bad tooth can not only alleviate your symptoms but also prevent further complications. Depending on the severity of the dental issue, treatment options may include root canal therapy, extraction of the tooth, or other necessary procedures.
In addition to seeking professional dental care, practicing good oral hygiene is essential for preventing tooth decay and infections. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
In conclusion, a bad tooth can indeed cause cold and flu-like symptoms. Understanding the connection between dental issues and systemic symptoms can help you identify the underlying cause of your illness and seek appropriate dental treatment. So, if you've been experiencing cold and flu symptoms, don't forget to consider the health of your teeth!
Oral Infections and the Impact on Respiratory Health
Did you know that an infected tooth can potentially cause cold and flu-like symptoms? It may come as a surprise, but our oral health is intricately linked to our overall well-being, including our respiratory health. Let's explore how oral infections can affect our respiratory system and what we can do to prevent and treat these infections.
When a tooth becomes infected, it means that bacteria have invaded the tooth's pulp, causing inflammation and pain. However, the effects of an infected tooth don't stop at the mouth. The bacteria can spread to other parts of the body, including the sinuses, throat, and even the lungs, leading to respiratory issues.
One of the ways an infected tooth can impact respiratory health is by causing sinusitis. The sinuses are hollow spaces in the skull, and they are connected to the nasal passages. When the bacteria from an infected tooth reaches the sinuses, it can lead to an infection, resulting in symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain, and a runny nose – similar to what you might experience with a common cold or flu.
Furthermore, an infected tooth can also contribute to the development of bronchitis and pneumonia. As the bacteria travel down the respiratory tract, they can reach the lungs and cause infections. This can lead to symptoms such as cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and even fever – all common signs of respiratory illnesses.
So, what can you do to prevent and treat oral infections to protect your respiratory health? Here are some tips:
Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, floss regularly, and use an antiseptic mouthwash to help kill bacteria in your mouth.
Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help identify and treat any potential oral infections before they become more serious.
Treat dental issues promptly: If you have a decaying or damaged tooth, seek immediate dental treatment to prevent the infection from spreading.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can help boost your immune system and keep you healthy overall, reducing the risk of infections.
If you suspect that an infected tooth is causing cold and flu-like symptoms, it's crucial to seek dental and medical attention. Your dentist can assess the tooth and recommend the appropriate treatment, which may involve a root canal or tooth extraction. Additionally, your doctor can evaluate your respiratory health and provide any necessary medication to treat any associated infections.
In conclusion, oral infections can indeed have an impact on respiratory health. It's essential to prioritize oral hygiene, visit your dentist regularly, and promptly address any dental issues to prevent the spread of bacteria and maintain good overall health. By taking care of your mouth, you can take significant steps towards safeguarding your respiratory system and enjoying a healthier, infection-free life.
Dental Health and the Immune System: A Link to Cold and Flu
When it comes to maintaining your overall health and well-being, often people forget about the important role oral health plays in the equation. Your mouth serves as the gateway to your body, and maintaining good dental health is crucial for a strong immune system.
One common dental issue that can have an impact on your immune system is a bad tooth. A bad tooth refers to a tooth that is decayed, infected, or damaged. If left untreated, a bad tooth can lead to a host of problems, including cold and flu-like symptoms.
Here are a few reasons why a bad tooth can cause symptoms similar to a cold or flu:
Infection: When a tooth becomes decayed or damaged, it creates an opening for bacteria to enter the tooth and cause an infection. This infection can spread to the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling, pain, and inflammation. These symptoms are similar to what you might experience during a cold or flu.
Sinus Involvement: Some bad teeth, particularly those in the upper jaw, can be closely related to the sinuses. When a tooth infection spreads to the sinuses, it can cause sinusitis, which presents symptoms similar to the common cold or flu. These symptoms may include congestion, facial pressure, headache, and a runny nose.
Weakened Immune System: Chronic infections, such as a long-standing bad tooth, can put strain on your immune system. Your immune system is responsible for defending your body against harmful bacteria and viruses. When it is constantly fighting an infection, it may become weakened, leaving you more susceptible to cold and flu viruses.
Spread of Bacteria: Bacteria from an infected tooth can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This can lead to systemic inflammation and further compromise your immune system. As a result, you may experience cold and flu-like symptoms, such as fatigue, body aches, and a general feeling of malaise.
Now that you understand the link between dental health and your immune system, it's important to take action to prevent and treat bad teeth.
(12/13/2024)by MedShun
More Information: https://medshun.com/article/can-a-bad-tooth-cause-cold-and-flu-symptoms
Views: 714
Do I Have a Cavity?: Six Warning Signs of Tooth Decay
Do you think you have a cavity? According to the CDC, over 90% of adults in the USA have had a cavity at some point in their lives.
Cavities are caused by plaque build-up on your teeth. Things that increase the likelihood of cavities are excess sugar, smoking, drinking alcohol, dry mouth, and improper brushing or flossing.
Most cavities can be easily treated. However, there are serious risks of tooth decay in untreated cases, including things like abscesses in the mouth or even gum disease.
Keep reading this guide to learn about the 6 warning signs of tooth decay.
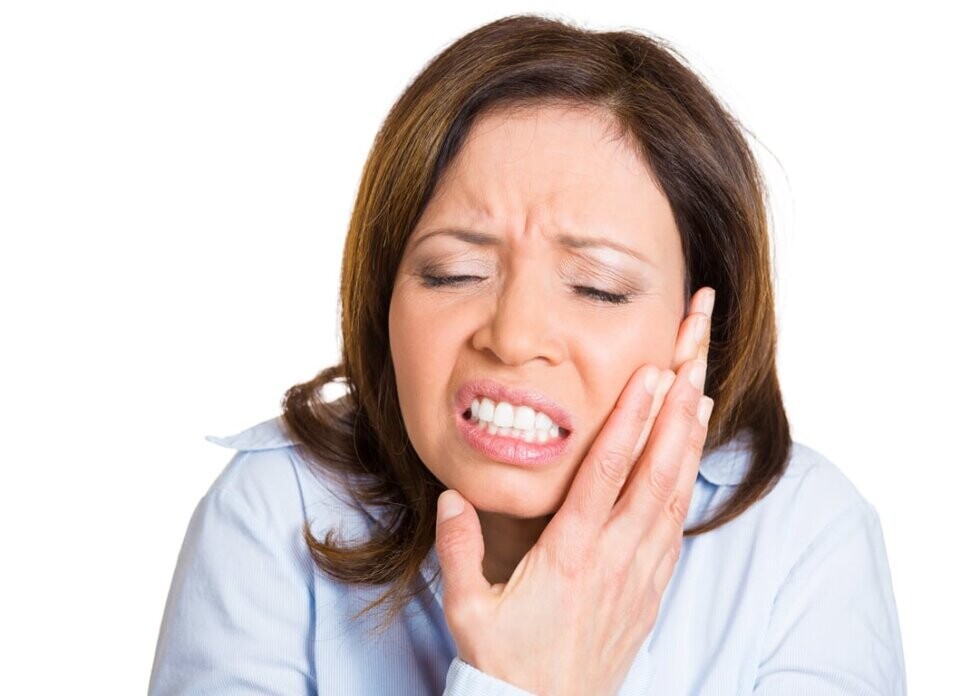

1) Toothache
Toothaches are typically the biggest red flag when it comes to cavities. The pain caused by a toothache may consist of pressure when you eat or it may consist of sudden and painful ache.
Short answer? If you have a toothache make sure you seek treatment to find out the cause.
2) Tooth Sensitivity
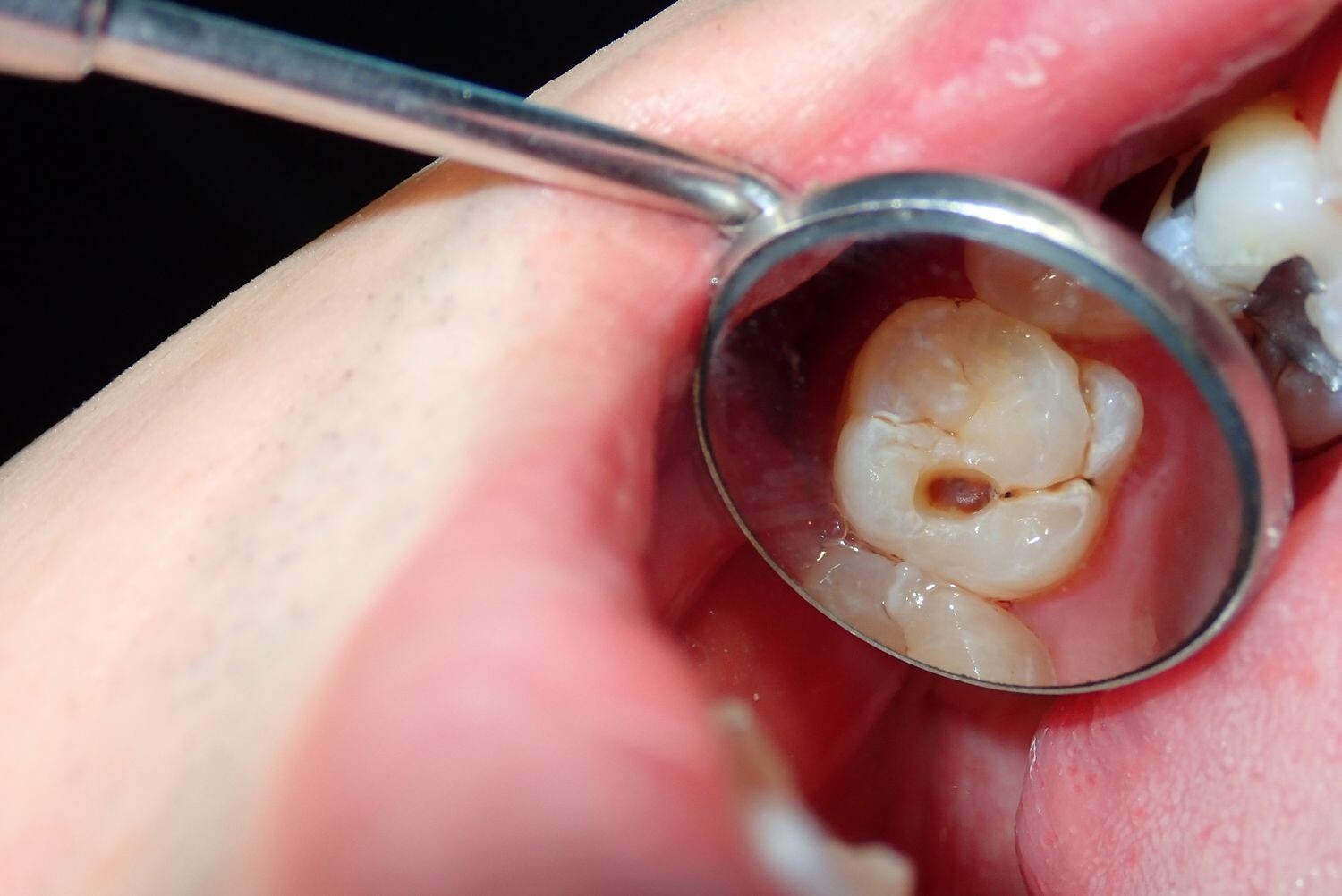
Tooth sensitivity is also one of the most common signs of a cavity. Dental sensitivity typically occurs when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages.
Likewise, sweet and sugary food and drinks may also cause pain or aches in your teeth.
If you notice that your teeth have become sensitive to temperature or sweets, you may very well have a cavity or other dental issue.
3) Teeth Staining
Notice any teeth staining? Unfortunately, stains on the teeth may also signify a cavity.
These stains may show up as white spots, but can be gray, brown, or even black as the cavity worsens. You may also notice redness in your mouth from dental inflammation.
4) Hole in Your Tooth
A hole in your tooth will usually occur in the later stages of untreated cavities. Most of the time you will be able to feel any holes in your teeth with your tongue.
You also may be able to visually notice them when brushing or flossing your teeth.
If you notice a hole in your tooth, see your dentist ASAP.
5) Bad Breath or Taste in Mouth
Sometimes, tooth decay will cause you to have bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth. Bacteria that are lodged between the infected tooth is usually the culprit.
These symptoms can be unpleasant to yourself and others. While it does not mean that you 100% have a cavity, it’s important to rule out the possibility.
6) Facial Swelling
Facial swelling is a less commonly known symptom of tooth decay but is possible. A tooth abscess caused by a cavity is usually to blame in this case.
So, if you notice one side of your face seems puffy and swollen, it’s important to find out the underlying cause.
Signs of Tooth Decay
Those were the 6 warning signs of tooth decay. If you’re wondering, “Do I have a cavity?” it’s important to be aware of any of these tooth decay symptoms and book a dental appointment as soon as you can.
(12/13/2024)by Dr. Parul Mehta, DDS
More Information: https://www.hi-techsmiles.com/do-i-have-a-cavity-6-warning-signs-of-tooth-decay/
Views: 562
Is UV Teeth Whitening Safe?
Everyone deserves to have a beautiful, confident, and healthy smile, so it’s no wonder that there are so many at-home products on the market that help you combat yellow or stained teeth to achieve a brilliant sparkle. But there’s one teeth whitening product that’s gained attention in the past decade among celebrities and social media influencers that’s a bit more high-tech and a bit more expensive: an at-home UV teeth whitening kit. Here, we’ve laid out a few facts on the safety and effectiveness of these types of products, so you can understand how it works before considering it as an option for a whiter smile.
How It Works
These kits are similar to a common in-office teeth whitening treatment, which involves a dental professional applying a peroxide-based whitening gel to your teeth, and placing a blue UV light over the teeth. Together, the gel and light create a system that can expedite the teeth whitening process. And these in-office treatments are effective—according to a study published in the Journal of Conservative Dentistry, light-activated bleaching showed an increase in lightness compared to bleaching done without light. Further, the light-activated process lasted longer.
An at-home kit functions similarly and typically instructs you to apply a whitening gel to your teeth with a pen and then use a portable LED light over your teeth for a few minutes over a period of days. These kits often come with a higher price tag than other at-home whitening solutions, like whitening toothpaste or strips.
Safety of UV Teeth Whitening Kits
You might be wondering: is UV teeth whitening safe? While the American Dental Association does mention that in-office light-activated treatments are an option you could consider for teeth whitening, they do not mention at-home UV light kits as a recommended option. The ADA also notes that tooth sensitivity may be associated with this process when done at the dentist’s office.
Another critical safety consideration: there are no regulations associated with at-home UV light teeth whitening kits. A 2019 article in the Journal of the American Dental Association states that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guidelines for Infection Control “do not include safety recommendations or regulations that are directly related to blue light exposure.”The article also concludes that evidence suggests you should take precautions when using dental curing kits. Further, according to the Oral Health Foundation, regulations on these kits vary from country to country. For instance, kits in Europe cannot legally contain more than 0.1% peroxide, whereas other countries allow for stronger amounts. Plus, some kits sold over the internet may contain extra ingredients that could be potentially harmful.
Another potential issue in using UV teeth whitening is that there can be extreme user error, resulting in damage and even burns. The ratio of gel to UV exposure varies from kit to kit, and without the consultation of a dentist, you may not know your threshold for sensitivity. What's more, applying too much gel at one time can result in the gel conducting too much of the heat from the UV light, causing gum burns.
So, to answer the question initially stated about safety, it’s unclear. Therefore you should avoid using UV light kits at home, as the research isn’t definitive enough to say that it’s safe. Plus, the ADA has not approved this kind of therapy.
What if I injured myself with an at-home UV whitening kit?
If you’ve experienced any injury from a UV whitening kit, don’t panic—your oral health care provider will know what to do. If you’re injured, contact your oral health care provider immediately, and have the kit on hand to provide any information. From there, they will be able to help determine the best treatment. Luckily, there are plenty of other safe and effective home whitening methods available—and they don’t break the bank either!
Teeth Whitening Alternatives
If you want to whiten at home, you’ve got options. One is to choose a toothpaste that contains a whitening ingredient, like hydrogen peroxide. You can use a whitening toothpaste every day for continuous whitening that becomes part of your oral care routine—no extra steps required. Whitening strips and pens are other options, though you should consult with your oral care professional to ensure that this is the safest method for your needs. While these methods won’t be as quick as an in-office treatment, you can take comfort in knowing that they’re safe. But before you go ahead and choose an at-home whitening option, talk to your oral care provider first, and together you can determine the best (and safest) method.
The next time you notice an advertisement or celebrity endorsement for a teeth whitening UV light kit, remember to take it with a grain of salt. With the right at-home treatment or even a treatment via your oral care provider, you can get the star power smile without the risk.
(12/12/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-in/oral-health/teeth-whitening/is-uv-teeth-whitening-safe
Views: 599
What Is Strep Throat?
Strep throat is a highly contagious infection caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria (Streptococcus pyogenes), common in children but affecting adults too. Strep throat symptoms include a sore throat and a fever, as well as throat swelling, a swollen uvula, or swollen tonsils.
Healthcare providers use several tests to diagnose strep throat. It is treated with antibiotics, while medications and home remedies can help people to cope with symptoms until the infection clears. It's uncommon, but strep throat can cause serious complications.
This article will talk about what strep throat is and how you catch it. You will also learn about how your healthcare provider can tell if you have strep throat and what treatments you might need. There are also some steps that you can take to prevent strep throat.
Strep Throat Symptoms

If you catch strep throat, you will usually start feeling sick two to five days after you are exposed to the bacteria that causes the infection. There are several symptoms of strep throat, but the most common is a very sore throat.
Other symptoms of strep throat are:
Difficulty swallowing or pain when swallowing (which might also be felt in the ear on the same side)
Fever (101° F or higher)

Red, swollen tonsils that may have white patches or streaks of pus on them
Tiny red spots on the roof of the mouth (called petechiae)
Swollen lymph nodes in the front of the neck
Chills
Fatigue
Headaches
Loss of appetite
Abdominal pain
How Long Is the Contagious Period of Strep Throat?
Strep throat is highly contagious through airborne particles, touching a contaminated surface, or sharing personal items like food utensils. You'll feel sick about two to five days after exposure. After 24 to 48 hours of taking antibiotics, the infection should no longer be contagious. Good hygiene practices, such as hand washing, will help with strep throat prevention.
What Can Be Mistaken for Strep Throat?
Strep throat is not the only infection that can cause a sore throat. In fact, viral illnesses that cause a sore throat are more common than strep throat.
There are a few ways that strep throat is different from a sore throat from a viral infection, and these symptoms can help you to know if you have strep throat.
Strep throat may start suddenly with a fever. Sore throats from viral infections tend to happen gradually. If you have strep throat, you usually do not have a cough. A sore throat from a virus is more likely to have a cough with it, along with other cold symptoms like:
A runny nose
A hoarse voice
An eye infection commonly called "pink eye" (conjunctivitis)
The main symptom of strep throat is a sore throat that starts suddenly with a fever and chills. Your tonsils might be red and swollen. They might also have white streaks or pus on them. You might also have fatigue and a headache, but cough is usually not a strep throat symptom.
Causes
Strep throat spreads in saliva or other body fluids that have group A Streptococcus bacteria in them. If someone who has strep throat coughs or sneezes around you, it can expose you to the bacteria as it spreads through the air. You can also pick it up if you touch people or objects with bacteria on them.
Strep throat is very contagious. It's easily spread from one person to another. Some people are more likely to catch strep throat than other people, including people with weak immune systems, people having chemotherapy, babies, and people who are pregnant.
If someone in your home catches strep throat, there are steps you can take to lower your chances of catching it:
Do not share personal items, like towels, drinking cups, and eating utensils, with the person who is sick.
Wash clothes and bedding in hot water.
Keep your hands clean (that means washing your hands correctly and often).
Can You Be Around Someone With Strep Throat?
Someone with strep throat has the bacteria in their saliva and other body fluids. If they cough or sneeze, they can easily spread it to people. Sharing drinks or touching objects they've used also spreads infection. Avoid catching it from someone in your home by not using the same personal items, washing clothes and bedding in hot water, and washing your hands often.
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider can usually tell if you have strep throat. An expert in throat health, called an otolaryngologist, can also diagnose the infection.
They will ask you about your symptoms and look at your throat and neck. They will look for signs of strep throat, including:
Redness, swelling, or white patches that look like pus in the throat or on your tonsils
A rash on your body that started on your neck and chest
Red spots on the roof of your mouth (petechiae)
Swollen tonsils (tonsillitis)
Lymph nodes that are swollen
Your healthcare provider might do some tests to figure out if you have strep throat. These strep throat tests may include:
A rapid strep test uses a sample of saliva from the back of your throat. The results only take a few minutes, but sometimes, they are not right. A rapid strep test might say that you do not have strep throat when you really do. This is called a false-negative test result.
A throat culture uses a sample of tissue taken from the back of your throat using a swab. The sample is sent to the laboratory where technicians will look at it to see if any bacteria is growing. The results take several days to come back, but it is the most accurate test for strep throat.
Treatment
Before your healthcare provider decides on treatment, they will want to make sure that you do not have a sore throat for another reason. For example, a viral illness cannot be treated with antibiotics.
However, if you have strep throat, it means you have a bacterial infection. In this case, you would need an antibiotic. There are different antibiotics that treat strep throat, including:
Amoxicillin
Penicillin
Clindamycin
Cephalosporin
Clarithromycin
Azithromycin (called a "Z-pack")
Your healthcare provider will look at your medical record and talk to you about your health before they decide which antibiotic to give you. For example, if you are allergic to penicillin, they can prescribe you a different kind of antibiotic.
Sometimes, antibiotics are not strong enough to clear up a strep throat infection. This is called antibiotic resistance. If you are being treated for strep throat but your symptoms do not get better, your healthcare provider will change your treatment.
You should stay home with strep throat until you've taken antibiotics for 24 to 48 hours. After that, you aren't contagious and can't spread strep throat to other people.
It is important to take your antibiotic prescription exactly as instructed. You need to finish all of the medication—even if you start to feel better.
If you stop taking the antibiotics too early, the infection might not clear up. Instead, it might get worse. You could also have serious complications from the infection.
Strep throat symptoms like fever, muscle aches, and a headache can usually be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) medicine like ibuprofen. Strep throat home remedies, like having cool drinks or ice pops, can also help to ease throat pain.
Getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and eating nutritious meals (even if it hurts to swallow) will also help your body to recover.
Does Strep Throat Go Away on Its Own?
Strep throat symptoms can go away without treatment, usually within a week, but strep throat that's left untreated can lead to more serious conditions. For example, children with a red-bump rash may have strep that's led to scarlet fever. It's important for people to be accurately diagnosed and treated by a healthcare provider.
(12/12/2024)by Very Well Health
More Information: N
Views: 617
Six Ways to Keep Your Gums Healthy
Having cavity-free teeth doesn’t mean you have healthy gums. Since it’s usually painless, you may not know if something is wrong with your gums. A few strategies can help you keep your whole mouth healthy.
When it comes to your mouth’s health, it’s not all about how straight your teeth are or how bright your smile is. You can’t forget about your gums!
What is gum disease?
Gum disease starts when plaque builds up under and along the gum line. Plaque is a sticky film-like substance that’s filled with bacteria. It can cause infections that hurt the gum and bone, leading to gum disease and tooth decay. Plaque also can cause gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis causes your gums to become:
inflamed
tender
red
swollen
prone to bleeding
Fortunately, since the bone and tissue holding the teeth in place aren’t impacted, this damage is reversibleTrusted Source.

You can also develop periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease. Periodontitis impacts the bones that hold your teeth in place. Left untreated, it can ruin the gums, bones, and tissues connected to your teeth.
The final stage of gum disease is advanced periodontitis. This is when the fibers and bone supporting your teeth are destroyed. It can impact your bite, and teeth may need to be removed.
According to the American Dental Association (ADA), signs that you might have gum disease include:
consistently bad taste or breath
separating or loose permanent teeth
gums that easily bleed
gums that are swollen, red, or tender
gums that have pulled away from your teeth
Gum disease is preventable. Here are a few ways you can help keep your gums healthy.
1. Floss
Floss at least once a day. This helps remove the plaque and food that’s beyond your toothbrush’s reach, according to the ADA. It doesn’t matter when you floss. Do it at night, do it in the morning, or do it after lunch… just do it!
2. Get regular dental cleanings
Your dentist can detect early gum disease symptoms if you see them on a regular basis. That way symptoms can be treated before they become more serious. A professional cleaning is the only way to remove tartar. It can also get rid of any plaque you missed when brushing or flossing. If you have gingivitis, brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings can help reverse it.
3. Quit smoking
Yet another reason for smokers to quit: Smoking is strongly associated with the onset of gum disease. Since smoking weakens your immune system, it also makes it harder to fight off a gum infection, say the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Trusted Source. Plus, smoking makes it more difficult for your gums to heal once they’ve been damaged.
4. Brush twice a day
Brush your teeth after every meal. This helps remove the food and plaque trapped between your teeth and gums. Scrub your tongue too, since it can harbor bacteria. Your toothbrush should have soft bristles and fit in your mouth comfortably, says the Mayo Clinic.
Consider a battery-powered or electric toothbrush. These can help reduce gingivitis and plaque more than manual brushing. Swap toothbrushes or toothbrush heads every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles start to fray.
Try an electric toothbrush today.
5. Use fluoride toothpaste
As for toothpaste, store shelves are lined with brands that claim to reduce gingivitis, freshen breath, and whiten teeth. How do you know which one is best for healthy gums? Make sure to choose toothpaste that contains fluoride and has the ADA seal of acceptance. After that, the flavor and color is up to you!
You can purchase toothpaste that contains fluoride online.
6. Use a therapeutic mouthwash
Usually available over the counter, therapeutic mouthwashes can help reduce plaque, prevent or reduce gingivitis, reduce the speed that tarter develops, or a combination of these benefits, according to the ADA. Plus: A rinse helps remove food particles and debris from your mouth, though it’s not a substitute for flossing or brushing. Look for the ADA seal, which means it’s been deemed effective and safe.
It doesn’t matter whether your brush, floss, or rinse first. Just do a good job and use the right products.
(12/11/2024)by Healthline
More Information: https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/ways-to-keep-gums-healthy?utm_source=ReadNext
Views: 564
What's The Difference Between Gingivitis And Periodontitis?
It’s normal for your mouth to contain bacteria. However, when the bacteria build up, gum disease can develop. Gum disease is caused by a buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that coats the teeth.
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis. It involves gum inflammation, but it doesn’t always cause symptoms. It’s possible to have gingivitis without realizing it.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. This is the more advanced stage of gum disease. It can damage the gums and lead to tooth loss over time.
To learn more about gingivitis and periodontitis, read on. We’ll explain the different symptoms and treatment, as well as how to prevent gum disease.

What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis, or gum inflammation, is mild gum disease. It typically causes minor issues, which might come and go. When treated early, the condition is reversible.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of gingivitis include:

red, swollen gums
gums that bleed when you floss or brush your teeth
gums that randomly bleed
Often, gingivitis causes no pain or other symptoms.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to minimize inflammation. Treatment includes:
Oral hygiene. This includes regular brushing and flossing — and using the right techniques when doing so. A dentist can show you how to properly brush and floss your teeth.
Professional dental cleaning. A dentist will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and gumline.
Antiseptic mouthwash. This prescription mouthwash contains chlorhexidine, which reduces bacteria in your mouth.
What is periodontitis?
Without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, or severe gum disease. Periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontium, which is the gum tissue and bone that keep your teeth in place. As the condition progresses, it can cause teeth to loosen.
Symptoms
Periodontitis happens in stages. The later the stage, the more severe the symptoms.
Symptoms of periodontitis include:
red, swollen gums
bleeding gums
sensitive teeth
sore gums
bad breath
loose teeth
teeth that change positions
pain during chewing
gums that recede (pull away) from the teeth
When the gums pull away from a tooth, they form spaces called gum pockets. These spaces can become infected.
Treatment
Because periodontitis is an advanced stage of gum disease, it requires additional treatment. Again, the goal is to reduce inflammation.
Treatment includes:
Oral hygiene. Maintaining oral hygiene can slow down periodontitis and prevent additional tooth loss.
Professional dental cleaning. A dentist will perform a deep cleaning. They’ll remove tartar and plaque from teeth and below the gumline, which can help the gums reattach to the teeth.
Antibiotics. In severe cases, your dentist might prescribe oral antibiotics or apply a topical antibiotic.
Open surgery. During this procedure, your dentist cuts open the inflamed gums and cleans the root of the tooth. Next, they stitch the gum tissue together so it can reattach to the teeth.
How does gingivitis progress to periodontitis?
If gingivitis is left untreated, the plaque can accumulate and spread to the gumline. Bacteria in the plaque release toxins, which irritate and inflame the gums.
This triggers a chronic inflammatory response in the body, which damages the gum tissue and bone that keep the teeth in place. The result is periodontitis.
As the gums break down, they pull away from the teeth, creating gum pockets. These gaps can become infected by bacteria in the mouth, causing even more tissue damage.
The tissue damage can also make the gum pockets deeper. If the gaps become too big, the teeth may loosen due to bone loss. Deeper pockets may also mean it’s harder to reach the bacteria when you brush and floss.
What are the risks for gingivitis and periodontitis?
The following factors can increase your risk for gingivitis and periodontitis:
not maintaining oral hygiene
smoking or chewing tobacco
substance use
genetics
misaligned teeth that are difficult to clean
stress
lack of nutrients
puberty
pregnancy
hormone changes
certain medical conditions, like diabetes or HIV
some medications, like steroids or cancer therapy drugs
What are the causes of gingivitis and periodontitis?
The most common cause of gingivitis and periodontitis is a buildup of plaque.
The bacteria in the plaque “eat” sugars in your mouth, then release waste byproducts. These byproducts can irritate your gums and cause inflammation.
Other factors affecting gum disease include:
Hormone changes. During pregnancy, changes in hormones may increase the inflammatory response of gum tissue. Similarly, hormone fluctuations during puberty might make gum tissue more susceptible to plaque-related inflammation.
Medications. Some prescription drugs might enlarge the gums, making teeth more difficult to clean. Other medications might reduce saliva, which normally helps clean the teeth and control bacteria.
Nutrition. A low intake of vitamin C or high intake of refined carbohydrates can increase inflammation in gum disease.
How to prevent gingivitis and periodontitis
You can prevent gingivitis and periodontitis by maintaining oral hygiene. When done consistently, an oral hygiene routine can prevent plaque from building up and causing gum disease.
Oral hygiene basics
A good oral hygiene routine includes:
brushing your teeth twice per day
flossing between your teeth every day
eating a balanced, nutritious diet
scheduling routine dental cleanings
not smoking
When to see a dentist
In addition to your regular visits, you should see a dentist if you have:
red or swollen gums
bleeding while flossing, brushing, or eating
painful gums
separating gums
loose teeth
persistent bad breath
pain while chewing
teeth that look longer than usual (due to receding gums)
If you already have gum disease, be sure to attend your follow-up appointments. This is especially important if you have received treatment for periodontitis, which requires follow-up care.
Outlook
The outlook for gum disease depends on the stage.
Gingivitis is reversible. It can go away with proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleaning. If gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, you’ll need additional treatment. The exact outlook also depends on the severity of periodontitis.
Generally, early periodontitis is easier to treat and control. Early treatment reduces the risk of damage and tooth loss. If you have periodontitis, it may mean more frequent trips to the dentist so they can monitor your condition.
In both cases, you’ll have to maintain oral hygiene habits at home. Visit your dentist regularly for the best outlook. During each visit, your dentist can identify early signs of gingivitis before it progresses.
(12/11/2024)by Healthline
More Information: N
Views: 630
How To Reverse Gum Loss Naturally?
What Causes Receding Gums?
In this oral surgery, the dentist takes tissue from the roof of your mouth and attaches it to your gum line. The objective here is to cover the exposed roots of your teeth to guard them from harm. For extraordinarily damaged gums, gum graft surgery can help restore some misplaced tissue. The best approach to treat gum recession is to forestall it happening within the first place.
How Can You Reverse Gum Loss?
It is enough to mix solely a pinch of salt and heat water and rinse it within the oral cavity. In addition, it is desirable to rub with a little clove oil for inflamed gums. In addition, as an alternative of oil, the uncooked nail can be used by chewing to release its liquid that impacts the infected gums. This home remedy has been shown to scale back swelling, swelling, pain and bleeding of the gums. Pinhole surgical technique is an innovative surgical procedure for receding gums. During PST, your dentist makes a tiny hole in your gum tissue above the exposed tooth root.

And while receding gums can’t grow back, there are ways to catch gum recession early and forestall it from getting worse. A traditional gum grafting procedure entails excising tissue from the roof of the patient’s mouth and using it to cover the exposed root. Dr. Lamas can cover one or two teeth during this sort of procedure.
Reverse Gum Loss
Healthy gums fit snugly round your teeth and cover the sensitive roots. But hundreds of thousands of Americans have receding gums, a situation that makes gum tissue loosen and pull back from teeth, exposing them to break and decay. In superior stages of periodontitis, the gums aren’t able to keep teeth in place, causing them to become loose, fall out, or require elimination by a dentist. Want to know more about How Do You Reverse Receding Gum Line?
This treatment is best for gentle circumstances, as it is mainly to stop additional gum recession. Regardless of the precise explanation for your receding gums, treatment is necessary for stopping further dental issues and complications. At home, you must adopt cautious dental hygiene habits.
This is becoming a very popular treatment choice because each the procedure and the outcomes occur very quickly. Dental professionals who know all about reversing periodontitis. Use a great every day vitamin supplement and make certain you might be obtaining the day by day minerals required. People can even ask their dentist for tips about modifying this method to handle their receded gums. When cleaning the inside surfaces of the entrance teeth, maintain the toothbrush vertically.
How To Reverse Receding Gum Line?
Many people don’t even realize that they have receding gums until it’s already occurring. However, should you discover any signs of gum recession, it’s important to contact your dentist immediately. The course of may be treated to each prevent additional injury and to repair any lack of gums. GGS helps prevent bone loss and the gums from receding further. It also can protect the previously exposed tooth roots from decay. Most importantly, receding gums can be a symptom of underlying dental problems, together with gum disease, and may increase the danger of tooth decay and tooth loss.
According to a examine, fluoride decreased the rate of tooth decay by a median rate of round 29%. Another examine came upon that living in a spot which does not have fluoridated water can enhance the prospect of tooth decay by as much as 32%. The subject of gum recession is a tricky one, especially as a end result of we are going to all face it sooner or later. If your dentist sees that at-home strategies haven’t cured your gingivitis, s/he could prescribe a round of antibiotics to battle the infection. Avoid typical mouthwash dangers by utilizing alternatives like natural mouthwash. Not only should you use a good, soft-bristled brush, you should discover the best way to keep in mind to alter it out typically.
Reverse Receding Gums Naturally
We also present tips on the way to slow and stop its development. Rinse your mouth with hydrogen peroxide and water resolution. The anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric gel may help prevent plaque formation and gingivitis that lead to receding gums.
There are several natural remedies for treating receding gums. However, you should all the time seek the guidance of along with your dentist to choose the most suitable resolution for you. A periodontist can determine the most effective course of treatment to keep away from wasting gum tissues and your teeth.
Reverse Receding Gums Naturally
Hormonal changes also can wreak havoc in your oral health. If you wear dentures, your dentist should ensure that they match correctly, as this can also result in problems. Have you ever puzzled what your dentist is doing when they’re poking around your teeth and calling out numbers to your dental hygienist? Also generally identified as receding gums, gum recession is an oral condition where the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth.
(12/10/2024)by Medium
More Information: https://www.andersonperiodontal.com/3-great-benefits-of-laser-gum-disease-treatment-bloomfield-hills-mi/
Views: 554
Do Cavities Cause Bad Breath?
Most people wake up in the morning with less than kissable breath. But when bad breath, also known as halitosis, interferes with your confidence and social life, it's time to figure out what's causing it. Do cavities cause bad breath? And is your oral care routine strong enough to keep bad breath away? Here's what may be causing your bad breath and how you can remedy it.
What Causes Bad Breath?
Bad breath results from an accumulation of germs in the mouth. According to a review in the Journal of Pharmacy and BioAllied Sciences (JPBS, the official publication of the Organization of Pharmaceutical Unity with BioAllied Sciences registered in India), when certain germs in the mouth interact with proteins in the saliva, this creates volatile sulfur compounds. The sulfur compounds are what we smell when we realise it's time to grab a mint. According to the JPBS review, bad breath can be caused by:
Poor oral hygiene that allows food debris to get trapped in the mouth

Gum problems and periodontitis
Germs on the tongue
Ear, nose and throat problems, including tonsillitis and sinusitis
Dry mouth
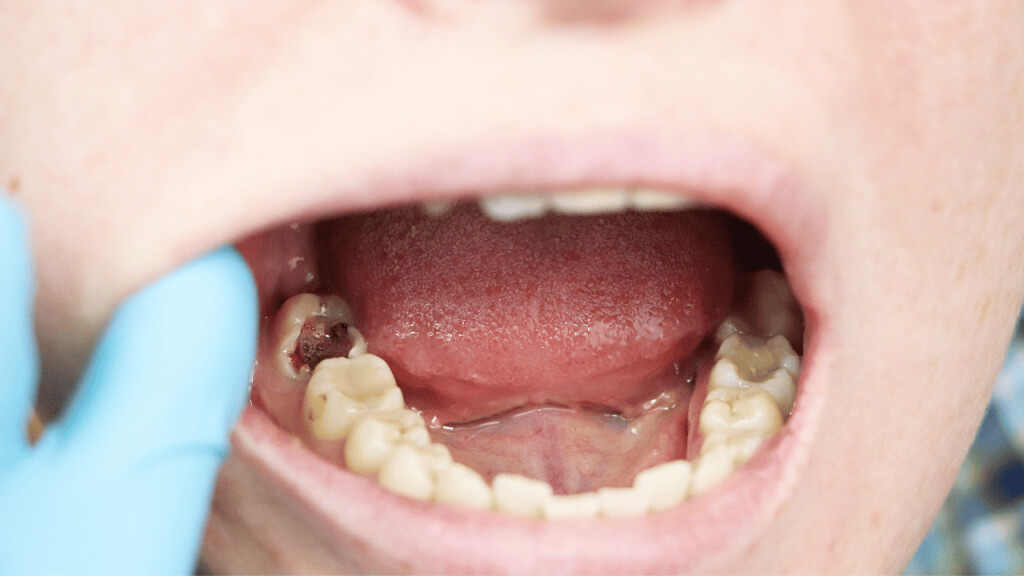
Personal habits, such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
Do Cavities Cause Bad Breath?
Cavities are small holes in the teeth where germs collect and eat away at the enamel. While cavities do not directly cause bad breath, they can contribute to it. Germs can get stuck and accumulate in the decay pockets, making it more difficult to keep your mouth clean and your breath fresh, explains the American Dental Association (ADA).
Bad breath does not necessarily signal a cavity, but it could indicate that you have one. That's why it's important to maintain regular dental appointments and see your dentist right away if you suspect that you have a cavity or if you are experiencing tooth sensitivity or pain.
Manage Bad Breath and Cavities Like a Pro
One of the easiest ways to manage and prevent both bad breath and cavities is to practise good oral hygiene. Start with brushing twice a day. Brushing your teeth physically removes decay-causing germs and food particles. You should also floss daily to remove lingering germs and food particles hiding in between your teeth.
Keeping your mouth moist is important for fresh breath, too. A healthy saliva flow is one of the best defenses against bad breath, as it washes out the mouth, notes the ADA. Be sure to drink plenty of water and talk to your doctor about any possible contributing factors for dry mouth, such as taking certain medications.
Smoking is another contributor to bad breath, and it can also increase your risk for gum problems, explains the ADA. Ask your doctor for strategies to help you quit.
If you wear dentures or another oral appliance, the US-based Mayo Clinic suggests cleaning them daily to prevent bad breath. Follow your dentist's specific directions for cleaning your appliance.
Finally, seeing your dentist regularly ensures that your mouth stays healthy. A professional teeth cleaning can remove germs and food that your toothbrush at home may miss. Your dental professional will also check for cavities that could harbour bad germs. If they do detect any cavities, they can fill them to stop the condition from worsening.
Bad breath can be a real bummer. While cavities do not directly cause bad breath, you can prevent both bad breath and cavities by practising good oral hygiene and seeing your dentist regularly.
(12/10/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/bad-breath/do-cavities-cause-bad-breath
Views: 575
If You Need Tooth Decay Treatment, Don't Wait
Even after trying your best to prevent tooth decay, sometimes the dentist finds a little cavity or two. It may be tempting to put off tooth decay treatment when you're not feeling any pain, but procrastination comes with a price: Tooth decay doesn't repair itself, and what starts out as a minor problem can quickly become serious, changing your treatment options dramatically.
The Start of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay refers to the damage of the teeth enamel. The enamel is the tough, external part of your teeth. This can be problematic to adults, teens and children. A sticky layer of film known as plaque continuously forms on the teeth. When you drink or eat foods containing sugars, these germs in the plaque manufacture acids which attack the tooth enamel. The sticky plaque helps keep the acids in contact with the teeth and after a period of time, the enamel breaks down.
Signs and Severity of Tooth Decay
You won't notice pain and sensitivity until decay goes through the enamel into the dentin layer. Dentin is made up of tiny nerve endings that become irritated and cause sensitivity when exposed to hot, cold, sweet, sticky and sour foods. You may also feel discomfort when biting down and find that food frequently gets trapped between your teeth.
Decay spreads rapidly through dentin because it is much softer than enamel. Root decay also spreads quickly, since the cementum covering on the root is not as hard and thick as enamel. Be warned that as tooth decay continues, your pain may be more frequent and intense.
It is important to remember that infection develops when decay and germs reach the pulp portion of your tooth, which contains the nerves and blood vessels. Pain from an abscessed tooth is persistent, serious and will likely keep you up at night. Other symptoms include fever, facial swelling and a bad taste in your mouth. You may notice pus draining from a red swelling on your gum near the root tip. Consequences can be serious if the infection spreads into your jawbone or throughout your body.
Tooth Decay Treatment
If your dentist detects a small area of erosion on your enamel before it reaches the dentin, he may suggest an approach that would help repair the spot. This process might include at home use remedies. Alternatively he may suggest using mouthwashes, toothpastes or filling materials that contain fluoride, calcium and phosphates.
When decay reaches the dentin, there is no turning back. A small cavity can be repaired with either an amalgam filling (composed of silver and other metals) or a tooth-colored resin material. If the tooth has lost a lot of its structure, however, your dentist may need to do a crown. Crowns strengthen and restore shape and function to your teeth, but they cost quite a bit more than a simple filling.
An abscessed tooth is the worst-case scenario, and your treatment options are slim: You can either opt for a root canal treatment or an extraction, though dentists will typically only do extractions when there are no other means of saving the tooth. Should you require a root canal, your dentist or an endodontist will remove the unhealthy pulp and clean and seal the pulp chamber. After root canal treatment, teeth can become more brittle and break easily. If you lost a lot of tooth structure due to decay, your dentist may also recommend a crown for your tooth.
Do you see a pattern here? The longer you put off dental treatment, the more involved and expensive it becomes — and the more pain you may have to endure. The moral of this story is to go to the dentist at the first sign of trouble. Better yet, help prevent decay from occurring by brushing and flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for a more thorough cleaning and checkup.
(12/09/2024)by Colgate
More Information: https://www.colgate.com/en-za/oral-health/cavities/if-you-need-tooth-decay-treatment-dont-wait
Views: 542
The Connection Between Dentists and Doctors
Dentists and doctors have more in common than supplemental schooling and white coats. Between oral and overall health, your body works as a system. Oftentimes 1 health issue can cross over to these 2 professions. Though dentists are trained in teeth, oral health issues can signal serious systemic illnesses. How dentists can help doctors detect a diagnosis:
Diabetes and Gum Disease
14% of New Mexico’s population has diabetes. Those with the disease are at high risk for developing gum disease. And it’s a 2-way street. Gum disease makes it hard to control blood sugar levels, which can compromise overall health. And because symptoms are sometimes subtle, diabetes can go unnoticed for years. The mouth offers clear-cut signals of the disease, and your dentist is trained to spot these warning signs.
If you’re diabetic or pre-diabetic, take control of your oral health. Diabetics with gum disease who receive appropriate dental care are healthier and often experience a reduction in blood glucose levels.

HPV and Oral Cancer
Genital HPV, human papillomavirus, is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the U.S. and world, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s estimated that 90% of adults have been exposed to some form of the disease. Every sexually active person is at risk for contracting HPV. And HPV can cause oral cancer.
Your dentist is often your first line of defense when it comes to spotting oral cancer. He or she will check for signs during a routine exam. In addition to practicing safe sex, it’s important to stay on top of your preventive care visits with your doctor AND dentist.
Heart Disease and Gum Disease

In fact, researchers recently discovered a link between oral bacteria and heart disease. Rather than judging gum disease severity through inflammation and bleeding, dentists can now identify specific types of bacteria present in the mouth. This gives them the ability to detect a patient’s probability for heart complications.
Reduce your risk for heart disease! Keep your teeth healthy, exercise regularly and eat a balanced diet.
Dentists and doctors may be different, but they can both make a positive impact on your overall health.
(12/09/2024)by Delta Dental
More Information: N
Views: 835
How Can Psoriasis Affect The Mouth And Tongue?
Psoriasis can affect any area of the body, including the mouth and tongue. The condition can cause cracks on the tongue or smooth patches, a complication called geographic tongue.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes a person’s skin to grow faster than average, resulting in changes in skin color and, often, scaly patches.
These patches can form anywhere on the body. Less frequently, psoriasis affects the mouth. Oral psoriasis can cause discolored patches with yellow or white edges to form on the tongue.
Read on to learn more about the symptoms, risk factors, and treatments for psoriasis on the tongue.
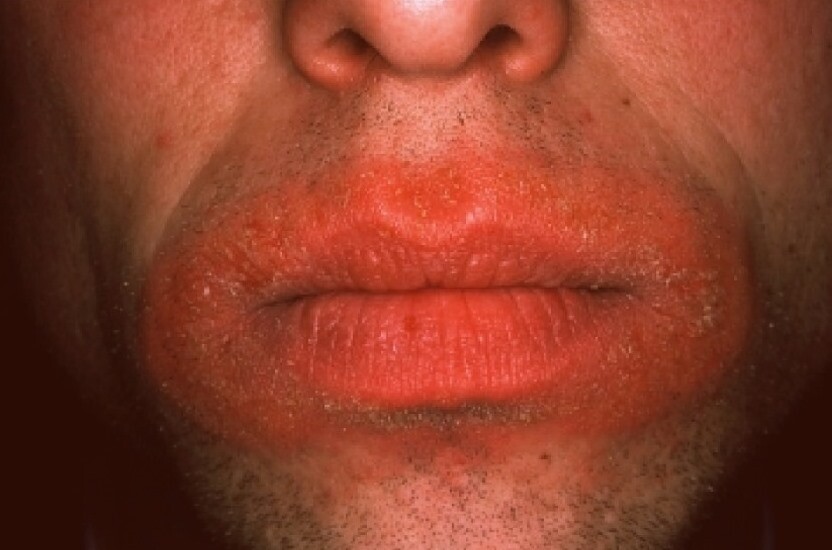
Symptoms of psoriasis on the tongue
Psoriasis can cause noticeable changes in the tongue’s color, texture, and feeling.
For example, people with psoriasis are more likely to develop an inflammatory condition called geographic tongue.
Although psoriasis on the tongue is rare, symptoms include:

discolored patches with yellow or white borders
swelling and discoloration on the tongue
smooth patches
fissures or cracks in the surface of the tongue
Psoriasis on the tongue can be tricky to diagnose because signs may be mild or even unnoticeable. However, for some people, these symptoms can lead to pain or swelling so severe that it makes eating or drinking difficult.
A thorough examination and testing can help a doctor determine if a person with a geographic tongue has oral psoriasis.
How does psoriasis affect the mouth, gums, and lips?
Psoriasis typically does not affect the mouth. When it does, people may experienceTrusted Source the following symptoms:
peeling skin on the gums
sores or pustules in or around the mouth
pain or a burning sensation when eating hot or spicy foods
a noticeable change in taste
In most cases, the patches or sores will appear inside the cheeks.
Risk factors for psoriasis on the tongue
To develop psoriasis, a person must have at least one relevant gene and experience exposure to triggers.
Several factors can triggerTrusted Source psoriasis, including:
stress
medications
infection
injury to the skin
Psoriasis may affect only one area of the body or several, and it may arise in new places. No matter where it occurs, psoriasis is not contagious, so a person cannot pass on the condition to others.
Treatment
Many treatments can helpTrusted Source people manage their psoriasis symptoms.
Oral psoriasis sometimes requires no treatment. However, consult a doctor if the symptoms interfere with daily activities.
For people with oral psoriasis, the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatories or topical anesthetics such as lidocaine. These medications can help reduce inflammation and pain, making it easier to eat and drink.
A person may notice improvements in oral psoriasis if they treat body-wide symptoms. Typically, when treating psoriasis, a doctor will prescribe medications such as:
non-biological medications, such as methotrexate
biological treatments, such as guselkumab
acitretin
cyclosporine
phototherapy
topical treatments such as steroid creams, emollients, or ointments.
Prevention
To prevent psoriasis symptoms from flaring up, it can help to avoid triggers. For psoriasis on the tongue, a person can:
avoid spicy or very hot foods
quit smoking
use mouth rinses
practice good oral hygiene
It can also help to reduce stress, which can worsen symptoms.
(12/07/2024)by Medical News Today
More Information: N
Views: 625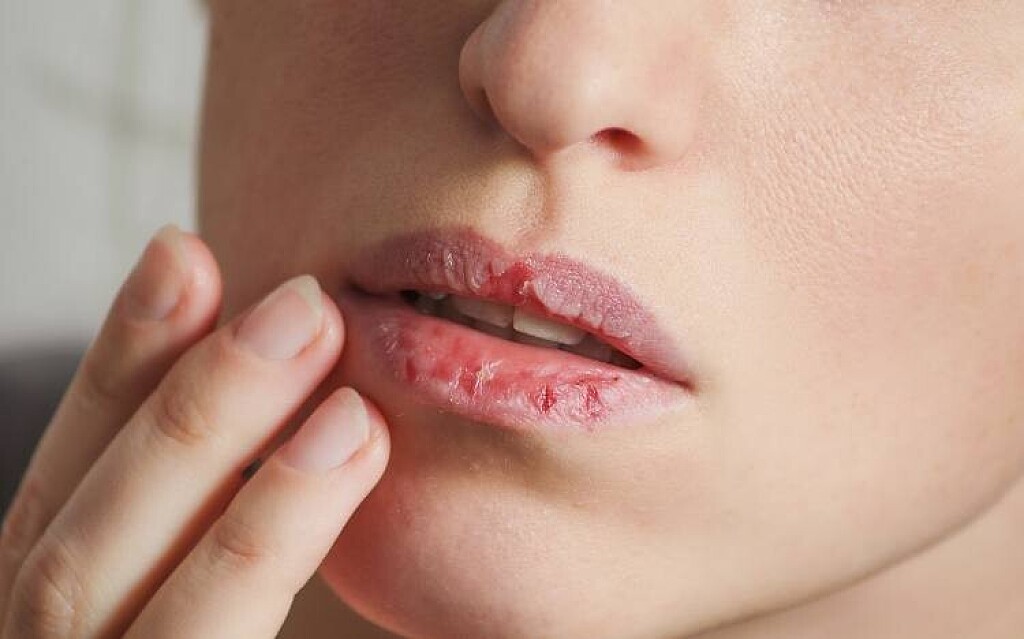
Can Diabetes Cause Dry Lips?
The answer to this question is simple – Yes, Diabetes can cause dry lips and dry mouth. It is more common in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes.
Dry lips and dry mouth are common occurrences in anyone’s life. It is experienced by diabetics too. But the difference is that when a diabetic person shares it, it is often not just something common or ignorable; it is rather a very serious symptom that needs to be catered to with attention.
It is easy to understand from the name that it is a condition where the mouth and lips feel dry and devoid of moisture. This can affect the individual. It is seen in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetic patients.
This is a problem that can also lead to other serious dysfunctions. Therefore, it must not be ignored.
A high blood sugar level in the body due to uncontrolled diabetic levels is often the cause behind a dry mouth and dry lips. This condition is termed – Xerostomia.

This is a very uncomfortable feeling. This symptom is often accompanied by other signs such as:
Dry tongue
Chapped and cracked lips
A Rough feeling inside the mouth
Sores and infections in the mouth

Painful gums
Trouble in swallowing food
Bruises and cracks
Bad breath
Now, we just had a look at what Dry lips in diabetes are. But what is the reason behind this? Let us find out.
How does Diabetes cause Dry lips?
We confirmed that prevailing diabetic conditions could be the reason behind dry lips. But you might be wondering … how are drying of lips linked to diabetes?
Well, let us now get into answering this essential question.
The primary reason diabetic patients experience a dry mouth is the fluctuating and often high blood sugar levels. When the body’s blood sugar levels see a sudden and unusual sugar level, it can lead to several different symptoms. One of them is dry lips and mouth.
Unmanaged high blood sugar levels can lead to the drying up of the lips. This can be caused by two reasons.
One of the reasons is the intake of high sugar foods that give rise to a high blood sugar level. The other reason is that improper production and release of insulin in the body can also drastically increase blood sugar levels.
The occurrence of dry lips can be either persistent or come and go every once in a while. This depends on when and how much your blood sugar level rises. If it is always at high ends, then it may lead to prevailing dry lips all the time.
These are the two main reasons that can lead to dry lips in diabetics.
Other explanations or causes of dry lips can be due to:
High blood pressure
Kidney issues
Dehydration
Medicines for blood pressure control
Antidepressant medicines
These other causes may often be linked to diabetes as well. This is because diabetes is a condition that leads to the development or severing of several bodily issues and ailments.
This has a tendency to become a serious problem and lead to discomfort. Thus, it is necessary to understand this condition well and take appropriate measures to manage it.
Let us have a look at what the effects of dry lips can be. Only when we know what the consequences of it are can we properly resolve the problem.
Here we go.
What are the effects of drying lips due to diabetes?
We now know what dry lips are, how they are connected to diabetes, and their causes. Now, let us go on to have a look at what the effects of dry lips and dry mouth can be.
The drying up of moisture in the mouth can be very uncomfortable. It has the following effects:
Drying mouth and lips is a cause for less saliva production, leading to discomfort in swallowing food or water.
Saliva in the mouth plays an important role in directing the food in its right path and keeping away bacteria and other microbes that may lead to harmful effects in the mouth.
Dryness in the lips results in cracked and chapped lips that can often be painful. If too severe, they can even bleed. It is also very uneasy and hampers with sensation.
Dry mouth and lips can also lead to gum sores, diseases, and infections. It can hamper daily eating too. Hence, it is very essential to keep a check on it all.
The risk of fungal infection in the mouth can also increase. There can be an infestation of oral yeast leading to inflammation and infection.
These problems and increasing symptoms can also give rise to tooth decay. This makes the diabetic condition even worse and adds several other issues to the health.
Hence, the negative effect of blood sugar problems can also have a drastic influence on the drying up of lips and mouth. The persistently high levels of carbohydrates in the body can contribute to other complications of health.
To keep away from these health-related discomforts, one must make sure to have a good meal and diet plan that suits their diabetic needs. Restrictions and medicines must be followed very efficiently to ensure protection and prevent the severing of these symptoms.
There are many other ways to keep away dry lips that are caused by diabetes. We have a list of tips and tricks that can help you overcome this dry lips and mouth issue.
Let us move on to look at these effective ways to deal with dry lips and mouth.
9 Easy Solutions to prevent of Dry Lips in Diabetes
Now you are aware of how and why this drying of the lips due to diabetes. And now, it is time to look at some preventive and curing measures to help your prevailing condition of dry lips and mouth.
It can create several uncomfortable issues and lead to bad maintenance of the teeth and gums, leading to many other problems. Therefore, it is very crucial to take into consideration the ways that can solve these problems.
We have some tips to include in your everyday schedules to ensure safety and keep your diabetic symptoms under check.
Here are 9 easy tips to get rid of them:
First of all, it is important to take your insulin doses properly. Insulin doses help to keep the blood sugar levels out of high risks of spiking. Thus, it can help to maintain the blood sugar levels and hence keep away other symptoms too. Also, make sure to attend your doctor’s and dentist’s appointments regularly.
This tip might seem too simple, but it is one that works the best. It is important to drink enough water all day. This is anyway a required criterion for diabetic patients besides;, it also helps with retaining moisture in the mouth. It is advisable to drink around 8 to 10 glasses of water per day.
If you are a frequent user of cigarettes, tobacco, and a regular alcohol drinker, it is necessary to pay attention to these things. They can also lead to dry lisp and mouth. The frequency of smoking and drinking must either be reduced or completely cut off.
If you live in a dry and dehydrating place, you can use a humidifier in your rooms to maintain a moist environment.
It is also aided well if you brush your teeth at least twice a day. This keeps the gums, tongue, and mouth safe and prevents any excess damage due to dry lips or mouth.
Flossing is a good way to let the mouth be clean and keep away any germs that may lead to infection. Possibly use an alcohol-free mouthwash for best results.
Sucking on mints, chewing gums, etc., can also keep the mouth protected from moisture loss. It also keeps the mouth cool and comfortable.
You can also use moisturizing lip care ointments that can prevent chapped lips and keep away the pain. There are many medicinal balms available too.
Include foods that have high fiber in them. They help keep the sugar levels low and controlled, leading to the prevention of other symptoms.
(12/07/2024)by Beat Diabetes
More Information: N
Views: 755My BEST Dentists Journal Headlines

